Press Release
World's darkest and clearest skies at risk from industrial megaproject
10 January 2025
On December 24th, AES Andes, a subsidiary of the US power company AES Corporation, submitted a project for a massive industrial complex for environmental impact assessment. This complex threatens the pristine skies above ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile’s Atacama Desert, the darkest and clearest of any astronomical observatory in the world [1]. The industrial megaproject is planned to be located just 5 to 11 kilometres from telescopes at Paranal, which would cause irreparable damage to astronomical observations, in particular due to light pollution emitted throughout the project’s operational life. Relocating the complex would save one of Earth's last truly pristine dark skies.
An irreplaceable heritage for humanity
Since its inauguration in 1999, Paranal Observatory, built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), has led to significant astronomy breakthroughs, such as the first image of an exoplanet and confirming the accelerated expansion of the Universe. The Nobel Prize in Physics in 2020 was awarded for research on the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way, in which Paranal telescopes were instrumental. The observatory is a key asset for astronomers worldwide, including those in Chile, which has seen its astronomical community grow substantially in the last decades. Additionally, the nearby Cerro Armazones hosts the construction of ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), the world’s biggest telescope of its kind — a revolutionary facility that will dramatically change what we know about our Universe.
“The proximity of the AES Andes industrial megaproject to Paranal poses a critical risk to the most pristine night skies on the planet,” highlighted ESO Director General, Xavier Barcons. “Dust emissions during construction, increased atmospheric turbulence, and especially light pollution will irreparably impact the capabilities for astronomical observation, which have thus far attracted multi-billion-Euro investments by the governments of the ESO Member States.”
The unprecedented impact of a megaproject
The project encompasses an industrial complex of more than 3000 hectares, which is close to the size of a city, or district, such as Valparaiso, Chile or Garching near Munich, Germany. It includes constructing a port, ammonia and hydrogen production plants and thousands of electricity generation units near Paranal.
Thanks to its atmospheric stability and lack of light pollution, the Atacama Desert is a unique natural laboratory for astronomical research. These attributes are essential for scientific projects that aim to address fundamental questions, such as the origin and evolution of the Universe or the quest for life and the habitability of other planets.
A call to protect the Chilean skies
“Chile, and in particular Paranal, is a truly special place for astronomy — its dark skies are a natural heritage that transcends its borders and benefits all humanity,” said Itziar de Gregorio, ESO’s Representative in Chile. “It is crucial to consider alternative locations for this megaproject that do not endanger one of the world's most important astronomical treasures.”
The relocation of this project remains the only effective way to prevent irreversible damage to Paranal's unique skies. This measure will not only safeguard the future of astronomy but also preserve one of the last truly pristine dark skies on Earth.
Notes
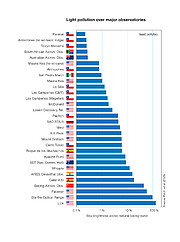
[1] A study by Falchi and collaborators, published in 2023 in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, compared light pollution at all 28 major astronomical observatories, finding Paranal to be the darkest site among them.
Contacts
Francisco Rodríguez
ESO Media Relations Officer
Santiago, Chile
Tel: +56 2 2463 3151
Email: francisco.rodriguez@eso.org
Bárbara Ferreira
ESO Media Manager
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6670
Email: press@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso2501 |
| Name: | Cerro Paranal, European Southern Observatory, Paranal |
| Type: | Unspecified : Technology : Observatory |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.