Press Release
First Image and Spectrum of a Dark Matter Object
HST and VLT Identify MACHO as a Small and Cool Star
5 December 2001
An international team of astronomers [2] has observed a Dark Matter object directly for the first time. Images and spectra of a MACHO microlens - a nearby dwarf star that gravitationally focuses light from a star in another galaxy - were taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (VLT). The result is a strong confirmation of the theory that a large fraction of Dark Matter exists as small, faint stars in galaxies such as our Milky Way.
The Riddle of Dark Matter
The nature of Dark Matter is one of the fundamental puzzles in astrophysics today. Observations of clusters of galaxies and the large scale structure of individual galaxies tell us that no more than a quarter of the total amount of matter in the Universe consists of normal atoms and molecules that make up the familiar world around us. Of this normal matter, no more than a quarter emits the radiation we see from stars and hot gas. So, a large fraction of the matter in our Universe is dark and of unknown composition .
For the past ten years, active search projects have been underway for possible candidate objects for Dark Matter. One of many possibilities is that the Dark Matter consists of weakly interacting, massive sub-atomic sized particles known as WIMPs. Alternatively, Dark Matter may consist of massive compact objects (MACHOs), such as dead or dying stars (neutron stars and cool dwarf stars), black holes of various sizes or planet-sized collections of rocks and ice.
The MACHOs
In 1986, Bohdan Paczynski from Princeton University (USA) realised that if some of the Dark Matter were in the form of MACHOs, its presence could be detected by the gravitational influence MACHOs have on light from distant stars.
If a MACHO object in the Milky Way passes in front of a background star in a nearby galaxy, such as the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), then the gravitational field of the MACHO will bend the light from the distant star and focus it into our telescopes. The MACHO is acting as a gravitational lens, increasing the brightness of the background star for the short time it takes for the MACHO to pass by.
Depending on the mass of the MACHO and its distance from Earth, this period of brightening can last days, weeks or months. The form and duration of the brightening caused by the MACHO - the microlensing "light curve" - can be predicted by theory and searched for as a clear signal of the presence of MACHO Dark Matter.
MACHOs are described as "microlenses" since they are much smaller than other known cases of gravitational lensing, such as those observed around clusters of galaxies. Observations of microlensing events have been done on many occasions with ESO telescope with intersting results, e.g., the recent detection of a corona of a distant star in the Milky Way.
The MACHO Project
Astronomers from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, the Center for Particle Astrophysics in the United States and the Australian National University joined forces to form the "MACHO Project" in 1991. This team [2] used a dedicated telescope at the Mount Stromlo Observatory in Australia to monitor the brightness of more than 10 million stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) over a period of eight years.
The team discovered their first gravitational lensing event in 1993 and have now published approximately twenty instances of microlenses in the direction of the Magellanic Clouds. These results demonstrate that there is a population of MACHO objects in and around the Milky Way galaxy that could comprise as much as 50% of the Milky Way total (baryonic/normal-matter) Dark Matter content.
Hubble obtains the first direct image of a MACHO
In order to learn more about each microlensing event, the MACHO team has used the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to take high-resolution images of the lensed stars.
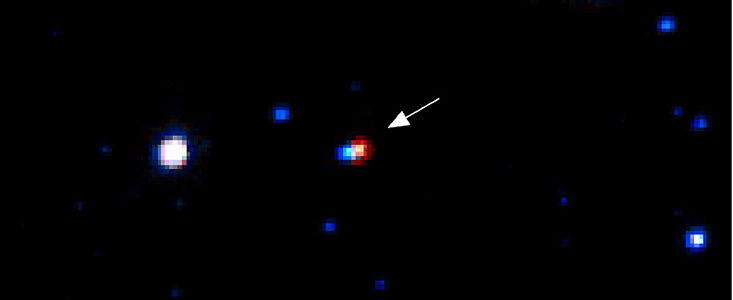
One of these images showed a faint red object within a small fraction of an arcsecond from a blue, normal (main-sequence) background star in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The image was taken by Hubble 6 years after the original microlensing event, which had lasted approximately 100 days. The brightness of the faint red star and its direction and separation from the star in the Large Magellanic Cloud are completely consistent with the values indicated 6 years earlier from the MACHO light curve data alone.
This Hubble observation further reveals that the MACHO is a small faint, dwarf star at a distance of 600 light-years, and with a mass between 5% and 10% of the mass of the Sun.
The VLT adds spectral information
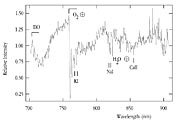
To further confirm these findings, members of the MACHO team sent in a special application for observing time on the FORS2 instrument on the ESO 8.2-m VLT KUEYEN Unit Telescope to obtain spectra of the object. ESO responded swiftly and positively to the request. Although it was not possible to separate the spectra of the MACHO and background star, the combined spectrum (ESO Press Photo eso0140) showed the unmistakable signs in the red spectral region of the deep absorption lines of a dwarf M star superimposed on the spectrum of the blue main sequence star in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The nature of Dark Matter
The combination of the microlensing light curve from the MACHO project, the high-resolution images from Hubble and the spectroscopy from the VLT has established the first direct detection of a MACHO object, to be published in the international science journal "Nature" on December 6, 2001.
Thanks to the HST and VLT observations, the astronomers now have a complete picture of this particular MACHO: its mass, distance and velocity. The result greatly strengthens the argument that a large fraction of the 'normal' Dark Matter in and around our galaxy exists in the form of MACHOs. Thus this Dark Matter is not as dark as previously believed!
Future searches for MACHO-like objects will have the potential to map out this form of Dark Matter and reach a greater understanding of the role that Dark Matter plays in the formation of galaxies. These efforts will further strengthen the drive to reveal the secrets of Dark Matter and take a large step towards closing the books on the mass budget of the Universe.
Notes
[1] This is a joint Press Release by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) and the Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international co-operation between ESA and NASA.
[2] The MACHO collaboration is made up of: Kem H. Cook, Andrew J. Drake, Stefan C. Keller , Stuart L. Marshall, Cailin A. Nelson and Piotr Popowski (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA); Charles Alcock and Matt J. Lehner (University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA); Robyn A. Allsman (Australian National Supercomputing Facility, Canberra, ACT, Australia); David R. Alves (STScI, Baltimore, USA); Tim S. Axelrod, Ken C. Freeman and Bruce A. Peterson (Mount Stromlo Observatory, Weston, ACT, Australia); Andrew C. Becker (Bell Labs, Murray Hill, NJ, USA); Dave P. Bennett (University of Notre Dame, IN, USA); Marla Geha (University of California at Santa Cruz, CA, USA); Kim Griest and Thor Vandehei (University of California, San Diego, CA, USA); Dante Minniti (P. Universidad Catolica, Santiago de Chile); Mark R. Pratt , Christopher W. Stubbs and Austin B. Tomaney (University of Washington, Seatlle, WA, USA); Peter J. Quinn (European Southern Observatory, Garching, Germany); Will Sutherland (University of Oxford, UK) and Doug Welch (McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada).
Contacts
Peter Quinn
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +4989-3200-6509
Email: pjq@eso.org
Cailin Nelson
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
USA
Tel: +1-925-423-2852
Email: cnelson@igpp.ucllnl.org
Dante Minniti
P. Universidad Catolica - Depto de Astronomia
Chile
Tel: +56 2 686 4946
Email: dante@astro.puc.cl
Tim Axelrod
Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics - Australian National University
Australia
Tel: +61-2-6125-0214
Email: tsa@mso.anu.edu.au
Lars Lindberg Christensen
Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49-89-3200-6306
Cell: +49-173-38-72-621
Email: lars@eso.org
Richard West
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49-89-3200-6276
Email: rwest@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0140 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 28/01 |
| Name: | Gravitational Microlensing, Spectrum |
| Type: | Milky Way : Cosmology : Phenomenon : Lensing Milky Way : Cosmology : Phenomenon : Dark Matter |
| Facility: | Hubble Space Telescope, Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | FORS2 |
| Science data: | 2001Natur.414..617A |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.