Persbericht
Most Massive Spiral Galaxy Known in the Universe
The VLT Observes Rapid Motion in Distant Object
8 december 2000
The most massive spiral galaxy known so far in the Universe has been discovered by a team of astronomers from Garching, Padova, Leiden, ESO and London [1]. They base their conclusion on recent observations with ISAAC, an infrared-sensitive, multi-mode instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope at the Paranal Observatory. This galaxy has been designated ISOHDFS 27 and is located at a distance of approx. 6 billion light-years (the redshift is 0.58). Its measured mass is more than 1000 billion times that of the Sun [2]. It is thus about four times more massive than our own galaxy, the Milky Way, and twice as heavy as the heaviest spiral galaxy known so far.
The determination of the mass of ISOHDFS 27 is based on a unique measurement of the motions of its stars and nebulae around the center. The faster the motion is, the greater is the mass. It is, in essence, the same method that allows determining the mass of the Earth from the orbital speed and distance of the Moon.
This is the first time a "rotation curve" has been observed in such a distant galaxy by means of infrared observations, allowing a very detailed dynamical study. Other observations by the team concern a pair of distant, interacting galaxies that were also found to possess comparably high masses. They also have observations of a third galaxy at a distance of about 10 billion light-years, with a mass that approaches that of ISOHDFS 27.
The new result has important cosmological implications, as it demonstrates that very heavy structures had already been formed in the Universe at a comparatively early epoch.
Star formation in young galaxies
It is of fundamental importance to current cosmological studies to understand how stars evolve within galaxies and how the galaxies themselves evolve into the various shapes we observe. Some are elliptical, others have the form of single or multiple spirals. Quite a few, especially smaller ones, appear to have no particular structure at all and are referred to as "irregular".
With the advent of large optical/infrared telescopes like the ESO VLT, astronomers are now able to observe extremely distant objects and hence to "look back" to the time when galaxies were being formed in the young Universe. They have found it particularly useful to observe in the infrared part of the spectrum during the present search for "young galaxies". Such observations minimize the effects of dust obscuration and serve to trace the active phases of galaxy evolution, i.e. those specific periods of time when there is particularly intense star-formation in a galaxy.
It is still not well known what triggers such phases of enhanced star-forming activity, but it is suspected that galaxy collisions and mergers may play an important role. The formation of stars usually takes place deep inside thick dust clouds that absorb the optical and UV light from the young stars and re-emit it in the infrared region of the spectrum. The imprints of this type of activity are thus best observed in that spectral band. Indeed, the infrared spectra of such objects have been found to undergo huge variations that relate to the related, complex processes.
Infrared observations are therefore crucial for the study of these most violent episodes in the Universe. By means of detailed observations of distant galaxies, we may hope to learn how they occurred at earlier times and, in particular, how the major structures (e.g., spirals, bulges) that we now see in most galaxies were formed.
Dusty Infrared-Luminous Galaxies
In 1995-98, the infrared camera ISOCAM onboard the ESA Infrared Space Observatory (ISO), with its unique imaging capabilities, provided astronomers with the first deep, overall "infrared view" of the Universe. Through various deep surveys with ISO, a new class of objects was discovered: luminous, distant galaxies detected during transient phases of enhanced infrared emission and undergoing rapid evolution with cosmic time.
One of the sky areas surveyed by ISO was the Hubble Deep Field South (HDF-S), that has also been observed with various ESO telescopes including the VLT, cf. eso9820.
The present team of astronomers decided to investigate some of the luminous galaxies that were detected by ISOCAM in the HDF-S area. Their goal was to better understand the enigmatic nature of these unsual objects and to try to learn which processes are really behind those huge amounts of energy that are emitted by these galaxies in the infrared region of the spectrum.
However, all of the galaxies in HDF-S are at very large distances - several billion light-years away (i.e. with redshifts between 0.6 and 1.5) and they are rather faint. They refer to these objects as ISOHDFS galaxies and their colours are quite red. The astronomers therefore decided to use one of the most efficient astronomical infrared instruments now available, the multi-mode ISAAC on the 8.2-m VLT ANTU telescope.
VLT Observations of ISOHDFS galaxies
In September 1999, the team began to obtain low-resolution spectra of about one dozen of these galaxies. This initial observing run at Paranal was very successful and it provided a first clue towards the true nature of these systems. It was found, in particular, that ISOHDFS galaxies emit strongly in the H-alpha spectral line from hydrogen atoms and that this emission originates in dusty regions with intense star formation activity in these galaxies.
The astronomers determined accurate redshifts (and hence, distances to the individual galaxies) by measuring the Doppler shifts of the H-alpha lines in their infrared spectra (an example of an early observation of this type is shown in ESO Press Release eso9856).
Inspired by the excellent quality of these first VLT observations, they were ready to take the next, challenging step in August 2000. They now attempted to get a deeper insight into the nature and dynamical stage of the ISOHDFS galaxies, by means of measurements of the stellar masses in the nuclear regions of these objects.
The spectrum of ISOHDFS 27
The first target for this new study was a large spiral galaxy, designated ISOHDFS 27 and of which an HST image is shown in ESO Press Photo eso0040 . The superb observing conditions at Paranal - the seeing improved to the near-record value of only 0.2 arcsec during the acquisition of these data! - made it possible to obtain the first spatially resolved, infrared H-alpha spectra of some of the ISOHDFS galaxies, allowing for the first time a probe into the dynamical stage of these distant objects.
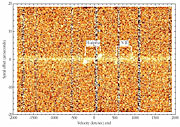
ESO Press Photo eso0041 shows the "raw" ISAAC spectrum, i.e. the image of the spectrum as seen in the read-out from the detector.
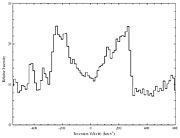
The derived spectral profile of the H-alpha line is shown in ESO Press Photo eso0041 . The shape is very unusual and implies that the emitting region is probably not concentrated at the centre of the galaxy, but most likely has a disk-like structure. Taking into account the inclination of the galaxy (50°), the difference in velocity between the two peaks is 830 km/sec, i.e. the rotational velocity is half of that, 415 km/sec, or significantly more than what is measured in normal spiral galaxies.
This was an interesting start for an ambitious project. But the astronomers got really excited when they made the first estimate of the total mass of that galaxy.
"I can't believe it, this spiral galaxy is really massive!" said Dimitra Rigopoulou from the Garching team. And she added: "With an estimated mass of 10 12 times that of our Sun and 4 times the mass of our own Galaxy, it seems to be the most massive spiral galaxy found so far in the Universe!" Indeed, careful calculations later showed that a total mass of 1.04 10 12 solar masses is present within 4 arcsec of the central region of (an area of 8 arcsec across), corresponding to 100,000 light-years (40 kpc) in ISOHDFS 27 . This is enormous by all standards [3]. The baryonic mass which corresponds to the mass in the older stars and is estimated from the infrared spectrum, is found to be 6 x10 11 solar masses, about half the dynamical mass.
During the same observing run, two other ISO-detected infrared sources were observed. One turned out to be a system of two counter-rotating galaxies with masses of about 2 x 10 11 solar masses and the other an even more distant galaxy (about 12 billion light-years) with comparably high mass.
Implications and Future Plans
The present programme is a fine illustration of the importance of "collaboration" between space- and ground-based telescopes. While the galaxies were first found with ISO and HST, it took the enormous light-gathering capability of the VLT to obtain a detailed spectrum and measure their masses.
Clearly, these exciting results have important implications for future studies of formation and evolution of galaxies, as well as the origin of the IR background.
The discovery of such massive spiral galaxies at very large distances implies that enormous structures were in place in the Universe, already some 6 billion years ago.
Galaxies like ISOHDFS 27 which are strongly emitting in the infrared region of the spectrum are presumed to contribute significantly to the observed infrared background radiation. Consequently, these new observations imply that the infrared background is largely made up of massive galaxies with recent star formation activity.
The team now plans to continue its work on the determination of the dynamical status of other high-redshift galaxies. These studies are indeed very timely since a plethora of future space- and ground-based missions such as NGST, SIRTF, FIRST and ALMA will be able to perform even more detailed follow-up observations of these objects.
The present observations open a new and exciting era in the study of the formation of galaxies in the young Universe.
Noten
[1] The project on exploring the dynamical stage of ISO-detected galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field South is being carried out by a large international collaboration led by astronomers from the Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik (MPE) in Garching (Germany) and the Padova University (Italy). Besides Dimitra Rigopoulou and Alberto Franceschini , the team includes Herve Aussel (Padova), Catherine Cesarsky (ESO), Reinhard Genzel (MPE), David Elbaz (Saclay, France), Michael Rowan-Robinson (IC, UK), Niranjan Thatte (MPE), and Paul van der Werf (Leiden, The Netherlands).
[2] 1 billion = 1,000 million = 10^9.
[3] Some other distant spiral galaxies have been found with masses in the range of 1 - 5 x 10^11 solar masses. The heaviest spiral galaxy known until now is UGC 12591, with a measured mass of 6 x10^11 solar masses.
Contact
Dimitra Rigopoulou
Max-Planck-Institut fuer Extraterrestrische Physik
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49-89-30000-3392
E-mail: dar@mpe.mpg.de
Over dit bericht
| Persberichten nr.: | eso0041 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 25/00 |
| Naam: | ISOHDFS 27, Spectrum |
| Type: | Early Universe : Galaxy : Type : Spiral Early Universe : Galaxy : Size : Giant |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | ISAAC |