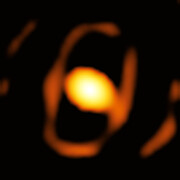Press Release
Astronomers take the first close-up picture of a star outside our galaxy
21 November 2024
“For the first time, we have succeeded in taking a zoomed-in image of a dying star in a galaxy outside our own Milky Way,” says Keiichi Ohnaka, an astrophysicist from Universidad Andrés Bello in Chile. Located a staggering 160 000 light-years from us, the star WOH G64 was imaged thanks to the impressive sharpness offered by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (ESO’s VLTI). The new observations reveal a star puffing out gas and dust, in the last stages before it becomes a supernova.
“We discovered an egg-shaped cocoon closely surrounding the star,” says Ohnaka, the lead author of a study reporting the observations published today in Astronomy & Astrophysics. “We are excited because this may be related to the drastic ejection of material from the dying star before a supernova explosion.”
While astronomers have taken about two dozen zoomed-in images of stars in our galaxy, unveiling their properties, countless other stars dwell within other galaxies, so far away that observing even one of them in detail has been extremely challenging. Up until now.
The newly imaged star, WOH G64, lies within the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the small galaxies that orbits the Milky Way. Astronomers have known about this star for decades and have appropriately dubbed it the ‘behemoth star’. With a size roughly 2000 times that of our Sun, WOH G64 is classified as a red supergiant.
Ohnaka’s team had long been interested in this behemoth star. Back in 2005 and 2007, they used ESO’s VLTI in Chile’s Atacama Desert to learn more about the star’s features, and carried on studying it in the years since. But an actual image of the star had remained elusive.
For the desired picture, the team had to wait for the development of one of the VLTI’s second-generation instruments, GRAVITY. After comparing their new results with other previous observations of WOH G64, they were surprised to find that the star had become dimmer over the past decade.
“We have found that the star has been experiencing a significant change in the last 10 years, providing us with a rare opportunity to witness a star’s life in real time,” says Gerd Weigelt, an astronomy professor at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn, Germany and a co-author of the study. In their final life stages, red supergiants like WOH G64 shed their outer layers of gas and dust in a process that can last thousands of years. "This star is one of the most extreme of its kind, and any drastic change may bring it closer to an explosive end," adds co-author Jacco van Loon, Keele Observatory Director at Keele University, UK, who has been observing WOH G64 since the 1990s.
The team thinks that these shed materials may also be responsible for the dimming and for the unexpected shape of the dust cocoon around the star. The new image shows that the cocoon is stretched-out, which surprised scientists, who expected a different shape based on previous observations and computer models. The team believes that the cocoon’s egg-like shape could be explained by either the star’s shedding or by the influence of a yet-undiscovered companion star.
As the star becomes fainter, taking other close-up pictures of it is becoming increasingly difficult, even for the VLTI. Nonetheless, planned updates to the telescope’s instrumentation, such as the future GRAVITY+, promise to change this soon. “Similar follow-up observations with ESO instruments will be important for understanding what is going on in the star,” concludes Ohnaka.
More information
ESO’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer is able to combine light collected by the telescopes of ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), either the four 8-metre Unit Telescopes or the four smaller Auxiliary Telescopes, creating highly detailed pictures of the cosmos. Effectively, this makes the VLTI a “virtual” telescope with a resolution equivalent to the maximum distance between the individual telescopes. This process is highly complex and needs instruments especially dedicated to this task. Back in 2005 and 2007 Ohnaka’s team had access to the first generation of these instruments: MIDI. While impressive for its time, those observations with MIDI only combined the light from two telescopes. Now, researchers have access to GRAVITY, a second-generation instrument able to capture the light of four telescopes. Its improved sensitivity and resolution made the image of WOH G64 possible. But there is more to come. GRAVITY+ is a planned upgrade of GRAVITY which will be able to take advantage of different technological updates performed at the VLTI and VLT. With these, the VLTI will be able to see objects fainter and farther than ever before.
This research was presented in a paper to appear in Astronomy and Astrophysics (https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202451820).
The team is composed of: K. Ohnaka (Instituto de Astrofísica, Departamento de Física y Astronomía, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Andrés Bello), K.-H. Hofmann (Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, Bonn, Germany [MPIfR]), G. Weigelt (MPIfR), J. Th. van Loon (Lennard-Jones Laboratories, Keele University, United Kingdom), D. Schertl (MPIfR), S. R. Goldman (Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, USA).
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) enables scientists worldwide to discover the secrets of the Universe for the benefit of all. We design, build and operate world-class observatories on the ground — which astronomers use to tackle exciting questions and spread the fascination of astronomy — and promote international collaboration for astronomy. Established as an intergovernmental organisation in 1962, today ESO is supported by 16 Member States (Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO’s headquarters and its visitor centre and planetarium, the ESO Supernova, are located close to Munich in Germany, while the Chilean Atacama Desert, a marvellous place with unique conditions to observe the sky, hosts our telescopes. ESO operates three observing sites: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its Very Large Telescope Interferometer, as well as survey telescopes such as VISTA. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. Together with international partners, ESO operates ALMA on Chajnantor, a facility that observes the skies in the millimetre and submillimetre range. At Cerro Armazones, near Paranal, we are building “the world’s biggest eye on the sky” — ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope. From our offices in Santiago, Chile we support our operations in the country and engage with Chilean partners and society.
Links
- Research paper
- Photos of the VLT and the VLTI
- For journalists: subscribe to receive our releases under embargo in your language
- For scientists: got a story? Pitch your research
Contacts
Keiichi Ohnaka
Universidad Andrés Bello
Santiago, Chile
Tel: +56-9522 39623
Email: k1.ohnaka@gmail.com
Gerd Weigelt
Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy
Bonn, Germany
Tel: +49 228 525 243
Email: gweigelt@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
Jacco van Loon
Keele University
Keele, UK
Tel: +44 1782 733331
Email: j.t.van.loon@keele.ac.uk
Bárbara Ferreira
ESO Media Manager
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6670
Cell: +49 151 241 664 00
Email: press@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso2417 |
| Name: | WOH G64 |
| Type: | Local Universe : Star : Circumstellar Material |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope Interferometer |
| Instruments: | GRAVITY |
| Science data: | 2024A&A...691L..15O |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.