Press Release
New Observations of Comet Hale-Bopp from La Silla
Methanol and Hydrogen Cyanide Detected at Record Distance
22 October 1998
Observations of famous Comet Hale-Bopp continue with the 15-m Swedish-ESO Submillimetre Telescope (SEST) at the La Silla Observatory. They show amazingly strong activity of this unusual object, also at the present, very large distance from the Sun. The radio observations document in detail the release of various molecules from the comet's icy nucleus. Of particular interest is the observed emission from methanol (CH 3 OH) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecules, never before detected in any comet this far away.
Comet Hale-Bopp still going strong
Just over 18 months after its perihelion passage on April 1, 1997, Comet Hale-Bopp (official designation C/1995 O1) is continuing its outward journey through the Solar System. It is now about 1,000 million kilometres (6.7 AU) from the Sun and the Earth, i.e. almost at the same distance as when it was first discovered in July 1995.
After having traversed the northern sky in 1996 and 1997, the comet passed the celestial equator in late June 1997 and is now seen in the southern constellation Volans (The Flying Fish), i.e. just east of the Large Magellanic Cloud. It can only be observed from southern latitudes.
The comet's brightness has decreased by a factor of more than 10,000 since it was at its brightest in March 1997, just before perihelion. However, the magnitude is still around 9 - 10, or only about 20-40 times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye. Hale-Bopp is therefore visible in binoculars to southern observers as a fuzzy object with a diameter of a few arcminutes.
New observations from La Silla
Several telescopes at La Silla are following the evolution of the activity of Comet Hale-Bopp as it recedes from the Sun. In particular, the comet is observed monthly with SEST, a 15-m diameter submillimetre telescope operated jointly by the Onsala Space Observatory (OSO, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden) and ESO; it is the only telescope of its type in the southern hemisphere.
Alternating each month, a Swedish team (headed by Anders Winnberg, OSO) and a European team (headed by Dominique Bockelée-Morvan, Observatoire de Paris) observe emission lines in the radio region of the spectrum from some of the molecules in the comet's coma (the cloud of gas and dust around the cometary "dirty-snowball" nucleus). These data are of great importance for understanding the mechanisms that are responsible for the outgassing (sublimation) of ices inside the nucleus of Comet Hale-Bopp.
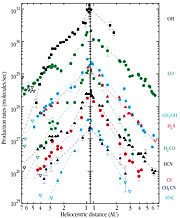
The observations began at SEST in September 1997 and constitute a follow-up programme of a long-term monitoring project at radio wavelengths that was started in August 1995 at the telescopes of the Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT), the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory (CSO) and the Nançay radio telescope by several teams of astronomers in Europe and US [1]. Radio emission from nine molecules in the coma were studied: H 2 O (water; by means of observations of the radical OH), CO (carbon monoxide), CH 3 OH (methanol), H 2 CO (formaldehyde), HCN (hydrogen cyanide), HNC (isomeric hydrogen cyanide), CH 3 CN (methyl cyanide), H 2 S (hydrogen sulphide) and CS (carbon sulphide).
Detection of methanol and hydrogen cyanide at record distance
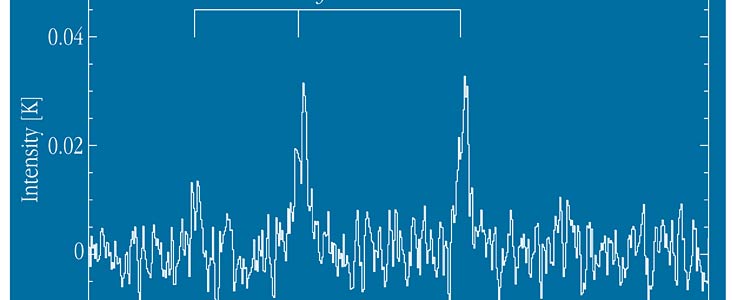
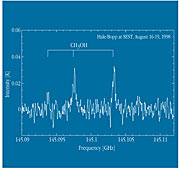
Observations at SEST were performed in July and August 1998 by Emmanuel Lellouch (Observatoire de Paris) and Marcus Gunnarsson (Uppsala Astronomiska Observatorium, Sweden), respectively. Three molecules were still detected : carbon monoxide (CO) at 230 GHz, hydrogen cyanide (HCN) at 89 GHz and methanol (CH 3 OH) at 145 GHz. On August 11, when Hale-Bopp was just over 900 million km (6 AU) from the Sun, no less than 2.4 · 10 28 CO molecules were released by the comet per second, corresponding to 1100 kg per second.
The measured production rates of HCN and CH 3 OH were about 200 and 20 times smaller, respectively. The observations of these two organic species at SEST constitute the most distant detections ever made in any comet.
The sublimation of water, the main constituent of cometary ices, is responsible for cometary activity within 3-4 AU from the Sun. However, at larger distances, this process ceases, due to the low temperature of the nucleus. At the present large distance from the Sun, the CO molecule is now the prime source of activity of Hale-Bopp.
When Comet Hale-Bopp was approaching the Sun before perihelion passage in 1997, the long-term monitoring programmes - in the radio wavelength region as well as in other spectral domains - clearly showed the transition from a CO - to a water-dominated coma, at about the time the comet came within 3-4 AU from the Sun. The CO -production rate now measured at SEST at 6 AU on the outward leg is about 100 times less than that at perihelion, and close to the value measured at the same distance from the Sun before perihelion.
While CO was first detected in Hale-Bopp in September 1995 at 6.8 AU from the Sun, only a few weeks after the discovery, HCN and CH 3 OH were not detected until a few months later, when the comet had approached to within 4.8-4.9 AU. It is likely that the convincing detection of these two molecules in August 1998 benefitted from an outburst (a sudden release of material from the nucleus) on August 15-19.
Some other species were observed at SEST out to a distance of 3-4 AU (H 2 S, CS, H 2 CO), but they are no longer easily detectable due to low production rates and the SEST sensitivity limit.
New data may provide a "look into the nucleus"
Comet Hale-Bopp provided the first opportunity in modern times to follow the activity of a comet over a very large range of heliocentric distances. The new data trace the gas release in some detail as the temperature and insolation change when the comet moves along its orbit. They show similarities and differences between individual molecules that in turn contain useful information about the physical state of cometary ices in the nucleus and its internal structure.
Some of the current key questions in this research field are concerned with the degree of separation of different ices ("chemical differentiation") in the upper layers of the nucleus, the form under which these ices co-exist and, not least, the still not understood production mechanisms at large heliocentric distances. These new observations will provide very valuable support to the theoretical studies of the cometary nucleus, now being undertaken by several research groups around the world.
The new observations of molecular lines in the radio spectral region also provide information about the temperature in the coma, if several lines of the same species are observed. Moreover, they serve to measure the expansion velocity of the gas and the outgassing pattern of the nucleus.
For instance, the observations of CH 3 OH in August 1998 show that the coma is now very cold at about 16 K (-257 o C). At perihelion (0.9 AU from the Sun), the corresponding temperature was of the order of 110 K (-163 o C). The expansion velocity has also considerably decreased since perihelion, from 1.1 km/sec to 0.5 km/sec. There is also evidence of anisotropic outgassing : more gas is seen to be flowing out from the sunlit hemisphere of the nucleus.
Observations continue
The monitoring of Comet Hale-Bopp at the SEST telescope will continue, at least until March 1999. The comet will then be nearly 1,200 million km (7.9 AU) from the Sun.
Observations are also made from time to time with other telescopes at La Silla. As an example, eso9849c was obtained a few days ago with the Danish 1.5-m telescope. It shows that a very complex coma structure is still present.
Due to the large size of the nucleus, probably 40 - 60 km in diameter, it will be possible to observe this comet with large optical telescopes for many years to come.
Information about Hale-Bopp on the web
Additional information about Comet Hale-Bopp is available on the web at many sites. Some of the most comprehensive websites may be accessed via the ESO Hale-Bopp site.
Notes
[1] Other scientists involved in the long-term radio monitoring of Comet Hale-Bopp are Nicolas Biver (Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, USA), Pierre Colom, Jacques Crovisier, Eric Gérard, Benoit Germain, Emmanuel Lellouch (Observatoire de Paris, France), Didier Despois (Observatoire de Bordeaux, France), Gabriel Paubert (IRAM, Granada, Spain), Raphael Moreno, Joern E. Wink (IRAM, Grenoble, France), John K. Davies (JAC, Hawaii, USA), William R.F. Dent (Royal Observatory, Edinburgh, UK), Hans Rickman, Marcus Gunnarsson (Uppsala Astronomiska Observatorium, Sweden), Per Bergman, Lars E.B. Johansson (OSO, Sweden), Fredrik Rantakyroe (SEST, La Silla), Darek C. Lis, David Mehringer, Dominic Benford, Martin Gardner, Tom G. Phillips (CSO, USA), Heike Rauer (DLR, Berlin, Germany).
[2] The figure appears in N. Biver et al. : "Long-term Monitoring of the Outgassing of C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp) at Radio Wavelengths", a poster paper presented at the DPS meeting on October 11-16, 1998 (Madison, Wisconsin, USA) and to be published in Vol. 30 of the Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society .
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso9849 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 16/98 |
| Name: | Comet Hale-Bopp, Spectrum |
| Type: | Solar System Solar System : Interplanetary Body : Comet Solar System : Interplanetary Body : Comet : Coma |
| Facility: | Swedish–ESO Submillimetre Telescope |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.