Press Release
Chronicle of a Death Foretold
Two of the World's Largest Interferometric Facilities Team-up to Study a Red Giant Star
31 May 2007
Using ESO's VLTI on Cerro Paranal and the VLBA facility operated by NRAO, an international team of astronomers has made what is arguably the most detailed study of the environment of a pulsating red giant star. They performed, for the first time, a series of coordinated observations of three separate layers within the star's tenuous outer envelope: the molecular shell, the dust shell, and the maser shell, leading to significant progress in our understanding of the mechanism of how, before dying, evolved stars lose mass and return it to the interstellar medium.
S Orionis (S Ori) belongs to the class of Mira-type variable stars. It is a solar-mass star that, as will be the fate of our Sun in 5 billion years, is nearing its gloomy end as a white dwarf. Mira stars are very large and lose huge amounts of matter. Every year, S Ori ejects as much as the equivalent of Earth's mass into the cosmos.
"Because we are all stardust, studying the phases in the life of a star when processed matter is sent back to the interstellar medium to be used for the next generation of stars, planets... and humans, is very important," said Markus Wittkowski, lead author of the paper reporting the results. A star such as the Sun will lose between a third and half of its mass during the Mira phase.
S Ori pulsates with a period of 420 days. In the course of its cycle, it changes its brightness by a factor of the order of 500, while its diameter varies by about 20%.
Although such stars are enormous - they are typically larger than the current Sun by a factor of a few hundred, i.e. they encompass the orbit of the Earth around the Sun - they are also distant and to peer into their deep envelopes requires very high resolution. This can only be achieved with interferometric techniques.
"Astronomers are like medical doctors, who use various instruments to examine different parts of the human body," said co-author David Boboltz. "While the mouth can be checked with a simple light, a stethoscope is required to listen to the heart beat. Similarly the heart of the star can be observed in the optical, the molecular and dust layers can be studied in the infrared and the maser emission can be probed with radio instruments. Only the combination of the three gives us a more complete picture of the star and its envelope."
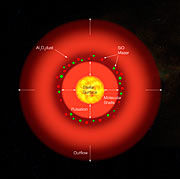
The maser emission comes from silicon monoxide (SiO) molecules and can be used to image and track the motion of gas clouds in the stellar envelope roughly 10 times the size of the Sun
The astronomers observed S Ori with two of the largest interferometric facilities available: the ESO Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) at Paranal, observing in the near- and mid-infrared, and the NRAO-operated Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), that takes measurements in the radio wave domain.
Because the star's luminosity changes periodically, the astronomers observed it simultaneously with both instruments, at several different epochs. The first epoch occurred close to the stellar minimum luminosity and the last just after the maximum on the next cycle.
The astronomers found the star's diameter to vary between 7.9 milliarcseconds and 9.7 milliarcseconds. At the distance of S Ori, this corresponds to a change of the radius from about 1.9 to 2.3 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun, or between 400 and 500 solar radii!
As if such sizes were not enough, the inner dust shell is found to be about twice as big. The maser spots, which also form at about twice the radius of the star, show the typical structure of partial to full rings with a clumpy distribution. Their velocities indicate that the gas is expanding radially, moving away at a speed of about 10 km/s.
The multi-wavelength analysis indicates that near the minimum there is more dust production and mass ejection: in these phases indeed the amount of dust is significantly higher than in the others. After this intense matter production and ejection the star continues its pulsation and when it reaches the maximum luminosity, it displays a much more expanded dust shell. This clearly supports a strong connection between the Mira pulsation and the dust production and expulsion.
Furthermore, the astronomers found that grains of aluminum oxide - also called corundum - constitute most of S Ori's dust shell: the grain size is estimated to be of the order of 10 millionths of a centimetre, that is one thousand times smaller than the diameter of a human hair.
"We know one chapter of the secret life of a Mira star, but much more can be learned in the near future, when we add near-infrared interferometry with the AMBER instrument on the VLTI to our (already broad) observational approach," said Wittkowski.
Notes
A maser is the microwave equivalent to a laser, which emits visible light. A maser emits powerful microwave radiation instead and its study requires radio telescopes. An astrophysical maser is a naturally occurring source of stimulated emission that may arise in molecular clouds, comets, planetary atmospheres, stellar atmospheres, or from various conditions in interstellar space.
ESO operates the Very Large Telescope Interferometer at Paranal Observatory, Chile, with four fixed 8.2-m telescopes and four relocatable 1.8-m telescopes, working at optical/infrared wavelengths. NRAO operates the Very Long Baseline Array with 10 stations across the U.S. working at radio wavelengths between 3 mm and 90 cm (0.3-90 GHz). ESO, NRAO and other partners will operate the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, working at millimetre wavelengths between 0.3 and 10 mm (30-950 GHz).
More information
The research presented here is reported in a paper in press in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics ("The Mira variable S Ori: Relationships between the photosphere, molecular layer, dust shell, and SiO maser shell at 4 epochs", by M. Wittkowski et al.). It is available in PDF format from the publisher's website.
The team consists of Markus Wittkowski (ESO), David A. Boboltz (U.S. Naval Observatory, USA), Keiichi Ohnaka and Thomas Driebe (MPIfR Bonn, Germany), and Michael Scholz (University of Heidelberg, Germany and University of Sydney, Australia).
Contacts
Markus Wittkowski
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6769
Email: mwittkow@eso.org
David A. Boboltz
U.S. Naval Observatory
USA
Tel: +1 202 762 1488
Email: dboboltz@usno.navy.mil
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0725 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 25/07 |
| Name: | S Orionis |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Evolutionary Stage : Red Giant |
| Facility: | NRAO Very Long Baseline Array, Very Large Telescope Interferometer |
| Instruments: | MIDI |
| Science data: | 2007A&A...470..191W |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.