Press Release
Black Hole in Search of a Home
Astronomers Discover Bright Quasar Without Massive Host Galaxy
14 September 2005
An international team of astronomers [1] used two of the most powerful astronomical facilities available, the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT) at Cerro Paranal and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), to conduct a detailed study of 20 low redshift quasars. For 19 of them, they found, as expected, that these super massive black holes are surrounded by a host galaxy. But when they studied the bright quasar HE0450-2958, located some 5 billion light-years away, they couldn't find evidence for an encircling galaxy. This, the astronomers suggest, may indicate a rare case of collision between a seemingly normal spiral galaxy and a much more exotic object harbouring a very massive black hole.
With masses up to hundreds of millions that of the Sun, "super massive" black holes are the most tantalizing objects known. Hiding in the centre of most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way, they sometimes manifest themselves by devouring matter they engulf from their surroundings. Shining up to the largest distances, they are then called "quasars" or "QSOs" (for "quasi-stellar objects"), as they had initially been confused with stars.
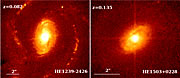
Decades of observations of quasars have suggested that they are always associated with massive host galaxies. However, observing the host galaxy of a quasar is a challenging work, because the quasar is radiating so energetically that its host galaxy is hard to detect in the flare.
To overcome this problem, the astronomers devised a new and highly efficient strategy. Using ESO's VLT for spectroscopy and HST for imagery, they observed their quasars at the same time as a reference star. Simultaneous observation of a star allowed them to measure at best the shape of the quasar point source on spectra and images, and further to separate the quasar light from the other contribution, i.e. from the underlying galaxy itself. This very powerful image and spectra sharpening method ("MCS deconvolution") was applied to these data in order to detect the finest details of the host galaxy.
Using this efficient technique, the astronomers could detect a host galaxy for all but one of the quasars they studied. No stellar environment was found for HE0450-2958, suggesting that if any host galaxy exists, it must either have a luminosity at least six times fainter than expected a priori from the quasar observed luminosity, or a radius smaller than about 300 light-years. Typical radii for quasar host galaxies range between 6,000 and 50,000 light-years, i.e. they are at least 20 to 170 times larger.
"With the data we managed to secure with the VLT and the HST, we would have been able to detect a normal host galaxy", says Pierre Magain (Université de Liège, Belgium), lead author of the paper reporting the study. "We must therefore conclude that, contrary to our expectations, this bright quasar is not surrounded by a massive galaxy."
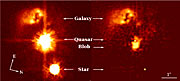
Instead, the astronomers detected just besides the quasar a bright cloud of about 2,500 light-years in size, which they baptized "the blob". The VLT observations show this cloud to be composed only of gas ionised by the intense radiation coming from the quasar. It is probably the gas of this cloud which is feeding the supermassive black hole, allowing it to become a quasar.
A strongly perturbed galaxy, showing all signs of a recent collision, is also seen on the HST images 2 arcseconds away (corresponding to about 50,000 light-years), with the VLT spectra showing it to be presently in a state where it forms stars at a frantic rate.
"The absence of a massive host galaxy, combined with the existence of the blob and the star-forming galaxy, lead us to believe that we have uncovered a really exotic quasar, says team member Frédéric Courbin (Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland). "There is little doubt that a burst in the formation of stars in the companion galaxy and the quasar itself have been ignited by a collision that must haven taken place about 100 million years ago. What happened to the putative quasar host remains unknown."
HE0450-2958 constitutes a challenging case of interpretation. The astronomers propose several possible explanations, that will need to be further investigated and confronted. Has the host galaxy been completely disrupted as a result of the collision? It is hard to imagine how that could happen. Has an isolated black hole captured gas while crossing the disc of a spiral galaxy? This would require very special conditions and would probably not have caused such a tremendous perturbation as is observed in the neighbouring galaxy.
Another intriguing hypothesis is that the galaxy harbouring the black hole was almost exclusively made of dark matter. "Whatever the solution of this riddle, the strong observable fact is that the quasar host galaxy, if any, is much too faint", says team member Knud Jahnke (Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, Germany).
The report on HE0450-2958 is published in the September 15, 2005 issue of the journal Nature ("Discovery of a bright quasar without a massive host galaxy" by Pierre Magain et al.).
Notes
[1] The team is composed of Pierre Magain and Géraldine Letawe (Université de Liège, Belgium), Frédéric Courbin and Georges Meylan (Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland), Pascale Jablonka (Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne and Université de Genève, Switzerland) , and Knud Jahnke and Lutz Wisotzki (Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, Germany).
Contacts
Pierre Magain
Institut d'Astrophysique de Geophysique, Université de Liège
Liege, Belgium
Tel: +32 4 366 97 53
Email: Pierre.Magain@ulg.ac.be
Pascale Jablonka
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Lausanne, Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 379 2469
Email: Pascale.Jablonka@obs.unige.ch
Lutz Wisotzki
Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam
Potsdam, Germany
Tel: +49 331 74 99 532
Email: lwisotzki@aip.de
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0529 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 23/05 |
| Name: | HE0450-2958, HE1239-2426, HE1503+0228 |
| Type: | Early Universe : Galaxy : Activity : AGN : Quasar |
| Facility: | Hubble Space Telescope, Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | FORS1 |
| Science data: | 2005Natur.437..381M |