Press Release
Weighing Ultra-Cool Stars
Large Ground-Based Telescopes and Hubble Team-Up to Perform First Direct Brown Dwarf Mass Measurement
15 June 2004
Using ESO's Very Large Telescope at Paranal and a suite of ground- and space-based telescopes in a four-year long study, an international team of astronomers has measured for the first time the mass of an ultra-cool star and its companion brown dwarf. The two stars form a binary system and orbit each other in about 10 years. The team obtained high-resolution near-infrared images; on the ground, they defeated the blurring effect of the terrestrial atmosphere by means of adaptive optics techniques. By precisely determining the orbit projected on the sky, the astronomers were able to measure the total mass of the stars. Additional data and comparison with stellar models then yield the mass of each of the components. The heavier of the two stars has a mass around 8.5% of the mass of the Sun and its brown dwarf companion is even lighter, only 6% of the solar mass. Both objects are relatively young with an age of about 500-1,000 million years. These observations represent a decisive step towards the still missing calibration of stellar evolution models for very-low mass stars.
Telephone number star
Even though astronomers have found several hundreds of very low mass stars and brown dwarfs, the fundamental properties of these extreme objects, such as masses and surface temperatures, are still not well known. Within the cosmic zoo, these ultra-cool stars represent a class of "intermediate" objects between giant planets - like Jupiter - and "normal" stars less massive than our Sun, and to understand them well is therefore crucial to the field of stellar astrophysics.
The problem with these ultra-cool stars is that contrary to normal stars that burn hydrogen in their central core, no unique relation exists between the luminosity of the star and its mass. Indeed, luminosities and surface temperatures of ultra-cool dwarf stars depend both on their age and their mass. An older, somewhat more massive ultra-cool dwarf can thus have exactly the same temperature as a younger, less massive one.
It is therefore a basic goal of modern astrophysics to obtain independently the masses of an ultra-cool dwarf star. This is in principle possible by studying such objects that are members in a binary system.
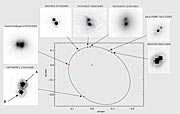
This is precisely what an international team of astronomers [2] has now done in a four-year long study of a binary stellar system with an ultra-cool dwarf star, using a plethora of top telescopic facilities, including ESO's Very Large Telescope, as well as Keck I and Gemini North in Hawaii and also the Hubble Space Telescope. This system - with the telephone number name of 2MASSW J0746425+2000321 [3]- is located at a distance of 40 light-years.
Beating the seeing
The astronomers used high-angular-resolution imaging to see both stars in the binary system and to measure their motion over a four-year period. However, this is more easily said than done, as the separation on the sky between the two stars is quite small: between 0.13 and 0.22 arcsec. This corresponds to the size of a 1-Euro coin, seen at a distance of about 25 km.
This separation is so small that it is normally not possible to differentiate the two stars due to the blurring effect of atmospheric turbulence (the "seeing"). It is therefore necessary to use the technique of adaptive optics. This wonderful method is based on the measurement of the image quality in real-time and sending corresponding corrective signals up to 100 times every second to a small deformable mirror, located in front of the detector. As the mirror continuously modifies its shape, the disturbing effect of the turbulence is neutralised. Applied at the VLT, this technique has resulted in images which are at least ten times sharper than the "seeing" and which therefore show many more details in the observed objects.
At the Very Large Telescope, the astronomers used the state-of-the-art adaptive optics NACO instrument [4]. Says Hervé Bouy, principal author of the paper presenting the results described here: "NACO offers the possibility to work in the infrared and is therefore ideally suited for the study of ultra-cool stars, which emit most of their light in this wavelength range. With the combination of the high efficiency of NACO and the VLT, and the excellent atmospheric conditions prevailing at Paranal, we were able to achieve very sharp images of this binary stellar system, almost as good as if the telescope were located in space."
Ultra-cool and on diet
During their four-year long study, seven different relative positions of the two components of the binary system were measured and Hervé Bouy and his co-workers were able to determine with good precision the stellar orbits. They find that the two stars revolve around each other once every 10 years and that their physical separation is only 2.5 times the distance of the Earth to the Sun - as astronomers say, 2.5 Astronomical Units. Using Kepler's laws, it is then straightforward to derive the total mass of the system. The obtained value is less than 15 % of the mass of the Sun.
The astronomers then used the photometric data of each star obtained in several wavebands, as well as spectra obtained with the Hubble Space Telescope to study the two objects in more detail. Using the latest stellar models of the group of the Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon, they found that both stars have roughly the same surface temperature, around 1500 °C (1800 K). For a star, this is ultra-cool indeed - by comparison, the surface temperature of the Sun is more than three times higher.
Using theoretical models, the team also found that the two stars are rather young (in astrophysical terms) - their age is between 500 and 1,000 million years only. The more massive of the two has a mass between 7.5 and 9.5% the mass of the Sun, while its companion has a mass between 5 and 7% of the solar mass.
Objects weighing less than about 7% of our Sun have been variously called "Brown Dwarfs", "Failed Stars" or "Super Planets". Indeed, since they have no sustained energy generation by thermal nuclear reactions in their interior, many of their properties are more similar to those of giant gas planets in our own solar system such as Jupiter, than to stars like the Sun.
The system 2MASSW J0746425+2000321 is thus apparently made up of a brown dwarf orbiting a slightly more massive ultra-cool dwarf star. It is a true "Rosetta stone" in the new field of low-mass stellar astrophysics and further studies will surely provide more valuable information about these objects in the transitional zone between stars and planets.
Notes
[1] This Press Release is issued in coordination with Astronomy & Astrophysics.
[2] The team is composed of Hervé Bouy (Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik; ESO Garching, Germany; and LAOG, Grenoble, France), Gaspard Duchêne (LAOG, Grenoble, France and UCLA, USA), Rainer Köhler and Wolfgang Brandner (Max-Planck Institut für Astronomie, Heidelberg, Germany), Jerome Bouvier and Xavier Delfosse (LAOG, Grenoble, France), Thierry Forveille (LAOG, Grenoble, France; and CFHT, Hawaii, USA), Eduardo Martin (IAC, Spain), Andrea Ghez and Caer-Eve McCabe (UCLA, USA), France Allard and Isabelle Baraffe (CRAL, Lyon, France), Gibor Basri (UC Berkeley, USA), and Laird Close (Steward Observatory, Arizona, USA).
[3] The name of the star comes from its appearance in the Working Point Source Databases of the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). 2MASS has uniformly scanned the entire sky in three near-infrared bands, achieving an 80,000-fold improvement in sensitivity relative to earlier surveys. The "J" in the name refers to the fact that the following numbers are the equatorial coordinates of the object in the sky for the standard equinox J2000.0.
[4] NACO is an abbreviation of NAOS/CONICA. The NAOS adaptive optics corrector was built, under an ESO contract, by Office National d'Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales (ONERA), Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Grenoble (LAOG) and the LESIA and GEPI laborator ies of the Observatoire de Paris in France, in collaboration with ESO. The CONICA infra-red camera was built, under an ESO contract, by the Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie (MPIA) (Heidelberg) and the Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE) (Garching) in Germany, in collaboration with ESO.
More information
The research described in this press release is published in the research journal Astronomy & Astrophysics ("First determination of the dynamical mass of a binary L1.5 dwarf" by H. Bouy et al.). The paper is available in PDF format on the publisher web site.
Contacts
Hervé Bouy
Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 30000 3317
Email: hbouy@mpe.mpg.de
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0420 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 16/04 |
| Name: | 2MASS J07464256+2000321 |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Type : Brown Dwarf |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | NACO |
| Science data: | 2004A&A...423..341B |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.