Press Release
Infrared Halo Frames a Newborn Star
28 August 2003
Observations with the VLT of a star-forming cloud have revealed, for the first time, a ring of infrared light around a nascent star. The images also show the presence of jets that emanate from the young object and collide with the surrounding cloud.
The DC303.8-14.2 globule
A small and dark interstellar cloud with the rather cryptic name of DC303.8-14.2 is located in the inner part of the Milky Way galaxy. It is seen in the southern constellation Chamaeleon and consists of dust and gas. Astronomers classify it as a typical example of a "globule".
As many other globules, this cloud is also giving birth to a star. Some years ago, observations in the infrared spectral region with the ESA IRAS satellite observatory detected the signature of a nascent star at its centre. Subsequent observations with the Swedish ESO Submillimetre Telescope (SEST) at La Silla (Chile) were carried out by Finnish astronomer Kimmo Lehtinen . He revealed that DC303.8-14.2 is collapsing under its own gravity, a process which will ultimately result in the birth of a new star from the gas and dust in this cloud.
Additional SEST observations of the millimetre emission of carbon monoxide (CO) molecules demonstrated a strong outflow from the nascent star. A small part of the gas that falls inward onto the central object is re-injected into the surrounding via this outward-bound "bipolar stream" .
The structure of DC303.8-14.2
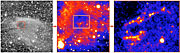
The left panel in ESO Press Photo eso0327 shows the DC303.8-14.2 globule as it looks in red light. This image was obtained at wavelength 700 nm and has been reproduced from the Digitized Sky Survey (DSS) [1]. It covers a sky region of 20 x 20 arcmin 2, or about 50% of the area of the full moon. The dust particles in the cloud reflect the light from stars, causing the cloud to appear brighter than the adjacent sky.
The brightness distribution over the cloud depends mostly on three factors connected to the dust. The first is the distribution of dust grains in the cloud, the way the dust density changes with the distance from the centre of the cloud. The second is the relative amount of light that is reflected by the dust particles. The third indicates the dominant direction in which the dust particles scatter light; this is dependent on the geometry of the grains and their preferred spatial alignment. Accurate observations of the brightness distribution over the surface of a globule allow an investigation of these properties and thus to learn more about the structure and composition of the cloud.
From the image obtained in red light (left panel in ESO Press Photo eso0327) it appears, somewhat surprisingly, that the brightest area of DC303.8-14.2 is not where there is most dust. Instead, it takes the form of a bright ring around the centre. This rim corresponds to a region where the intensity of the light from stars behind the cloud is reduced by a moderate factor of 3 to 5 when passing through the cloud and where the light-scattering efficiency of the dust grains in the cloud is the highest.
Observing with ISAAC on the VLT
In order to study the structure of DC303.8-14.2 in more detail, Kimmo Lehtinen and his team of Finnish and Danish astronomers [2] used the near-infrared imaging capabilities of the ISAAC multi-mode instrument on the 8.2-m VLT ANTU telescope at the ESO Paranal Observatory (Chile). Under good observing conditions, they obtained a mosaic image of this cloud in several near-IR wavelength bands, including the J- (centered at wavelength 1.25 µm), H- (1.65) and Ks-bands (2.17). These exposures were combined to produce images of DC303.8-14.2, two of which are shown in ESO Press Photo eso0327 (middle and right panels).
The middle image shows the central part of the globule in the H-band. A bright rim is clearly detected - this is the first time such a ring is seen in infrared light around a globule .
This rim has a smaller size in infrared than in visible light. This is because the absorption of infrared light by dust particles is smaller than the absorption of visible light. More dust is then needed to produce the same amount of scattering and to show a rim in infrared light. The infrared rim will therefore show up in an area where the dust density is higher, i.e. closer to the centre of the cloud, than the visible-light rim.
Similar rings were also detected in the J- and Ks-band images and, as expected, of different sizes. Thus the mere observation of the size (and shape) of a bright rim already provides information about the internal structure of the cloud. In the case of DC303.8-14.2, a detailed evaluation shows that the dust density of the centre is so high that any visible light from the nascent star in there would be dimmed at least 1000 times before it emerges from the cloud.
Getting a bonus: Jets from a young star
As an unexpected and welcome bonus, the astronomers also detected several jet- and knot-like structures in the Ks-band image (right panel in ESO Press Photo eso0327), near the IRAS source. The area shown represents the innermost region of the cloud (65 x 50 arcsec 2, or just 1/500 of the area of the DSS image to the left).
Several knot-like structures on a line like a string of beads are clearly seen. They are most probably regions where the gas ejected by the young stellar object rams into the surrounding medium, creating zones of compressed and hot molecular hydrogen. Such structures are known by astronomers as "Herbig-Haro objects".
Notes
[1] The Digitized Sky Survey was produced at the Space Telescope Science Institute under U.S. Government grant NAG W-2166. The images of these surveys are based on photographic data obtained using the Oschin Schmidt Telescope on Palomar Mountain and the UK Schmidt Telescope. The plates were processed into the present compressed digital form with the permission of these institutions.
[2] The team is composed of Kimmo Lehtinen, Kalevi Mattila from the Observatory of the University of Helsinki (Finland), Petri Väisänen from ESO/Chile and Jens Knude from the Observatory of the University of Copenhagen (Denmark). P. Väisänen is also affiliated with the University of Helsinki.
More information
A general description of the methods used to study and model surface brightness observations of small dark clouds in given in a basic paper by Kimmo Lehtinen and Kalevi Mattila in the research journal Astronomy & Astrophysics (Vol. 309, p. 570 1996). The results presented here will be published in a forthcoming paper in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Contacts
Kimmo Lehtinen
Observatory, University of Helsinki
Helsinki, Finland
Tel: +358-0-19122909
Email: kimmo.lehtinen@helsinki.fi
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0327 |
| Legacy ID: | Photo 26/03 |
| Name: | DC303.8-14.2 |
| Type: | Milky Way : Nebula : Appearance : Dark : Bok Globule |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | ISAAC |
| Science data: | 2003A&A...398..583L |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.