Release Notes¶
Summary¶
This release includes the following artefacts:
RTC Toolkit (
rtctk) - v1.0.0
And depends on the following:
ELT Development Environment (
ELT DevEnv) - v3.6.0Middleware Abstraction Layer (
CII MAL) - v1.6.0Common Integration Infrastructure Services (
CII SRV) - v1.3.0DDS Middleware (
FastDDS) - v2.4.0Application Framework (
rad) - v4.0.0-pre2Test Framework (
etr) - v3.1.0Roadrunner (
numappandipcq) - v0.1.0
What is the purpose of this release?¶
The purpose of this release is to provide a first basic working version of the toolkit to users to,
get a feeling how the RTC Toolkit, its modules and APIs function,
get familiar with core concepts, technologies and workflows,
facilitate early feedback from developers to correct issues and adapt the toolkit as early as possible.
What is the scope of this version?¶
To provide an early preview of the toolkit functionality, this release does not cover the full RTC Toolkit functionality.
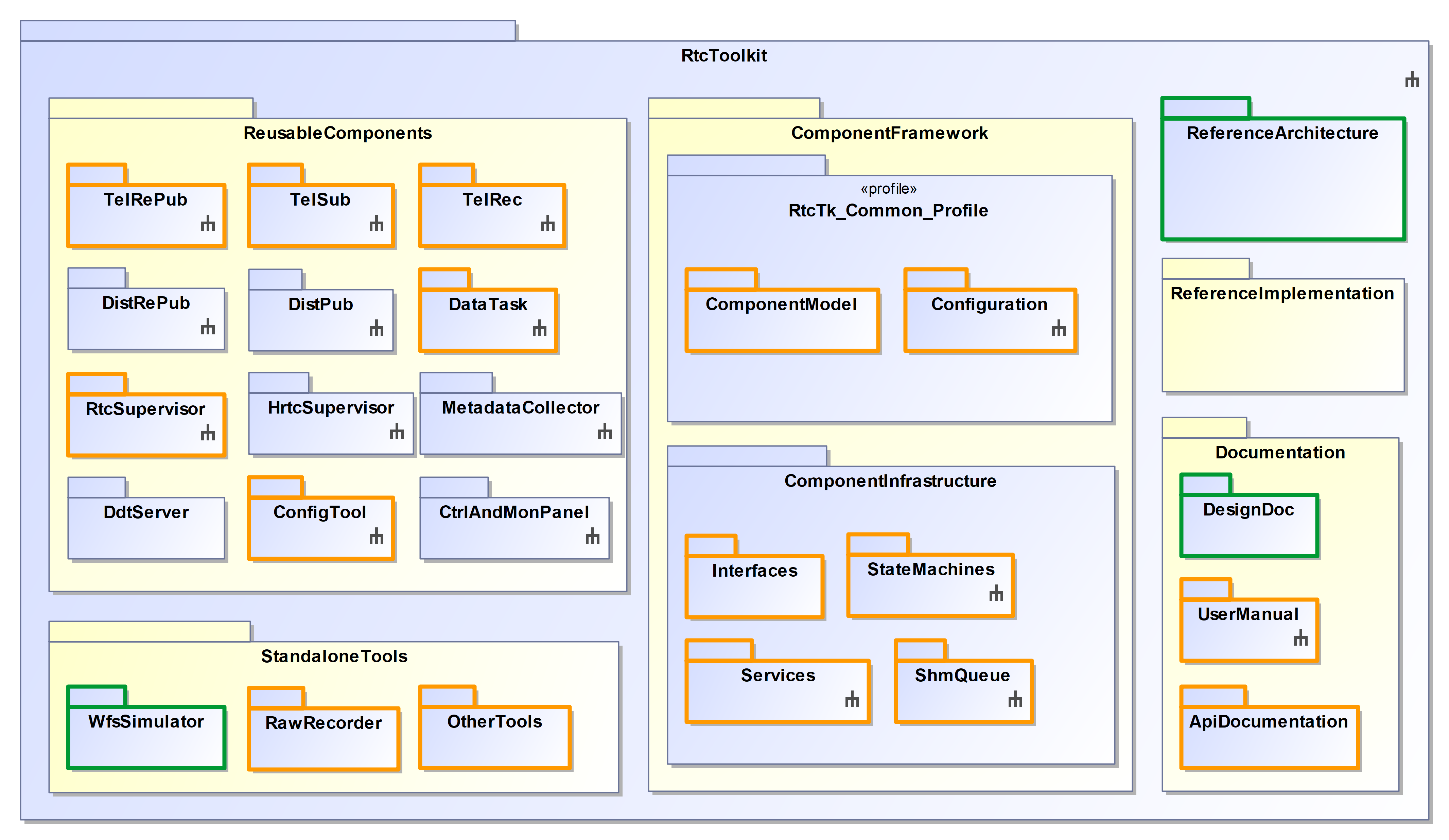
Assets that are not yet delivered with this version are depicted without a colored frame, assets that are part of this release but are not yet feature-complete are depicted with an orange frame. Assets that are part of this release and also considered feature-complete are depicted with a green frame.
The most important features of this release are:
Component Framework¶
RTC Component
Runtime Repository
Online Database
Service Discovery
Logging
Reusable Components¶
RTC Supervisor
Telemetry Republisher
Telemetry Subscriber
Telemetry Recorder
Data Task libraries
Examples and Tutorials¶
Creating bare RTC Components
Customising reusable components
Creating a minimalistic SRTC system
Creating a distributed minimalistic SRTC system
Other Features¶
CII MAL integration
CII OLDB integration
CUDA support in waf
Python support for Data Tasks
Manual Deployment (using scripts, optionally
Nomad)Use of
roadrunnerlibrariesSupporting Tools (for testing and troubleshooting)
Unit and Integration testing (using gTest and etr)
Documentation¶
User’s manual (using Sphinx)
API documentation (using Doxygen)
Limitations and Constraints¶
This version is still a show and tell with limited functionality to demonstrate basic functionality. The main focus was put on the development of basic building blocks and components that allow to showcase how a simple Telemetry Data Path can concretely be implemented.
No backward compatibility will be guaranteed for this release, breaking changes will still happen.
At the moment of the release not all of the underlying SW infrastructure is available e.g. deployment, and Core Integration Infrastructure (CII) are not fully functional yet. Therefore many of the services (e.g. deployment, configuration, logging, error handling, ..) had to be faked. This will be corrected in future versions as the underlying infrastructure and CII matures.
Currently only CII MAL and CII OLDB are used from the CII.
Since this release is only intended to demonstrate basic functionality, it is not optimised for performance and large data volumes.
For the same reason integration into a larger system is also not possible yet. In particular, very large vectors or matrices are not handled out of the box and require specialised CII OLDB configurations that are not available yet.
Disclaimer
ESO does not warrant that the provided functions of the RTC Toolkit will meet all requirements or that the operation of the components and libraries will be flawless.
ESO does not ensure that solutions included in this version of the RTC Toolkit are not subject to changes in future releases. The future upgrade to newer versions of ICS Framework, Core Integration Infrastructure (CII) and adaptation to CCS development standards may introduce significant modifications to the actual interfaces and services.
While every precaution has been taken in the development of the RTC Toolkit software and in the preparation of the documentation, ESO assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions, or for damage resulting from the use of the software or of the information contained in the documentation.
Note
The RTC Toolkit is distributed outside ESO for the development of applications related to the ELT Project and ruled by the “General Conditions of ESO Contracts”. Any other use is not permitted without prior authorization from ESO.
The rights of third party products, whose software is for convenience included in the development environment, are ruled by their copyright notice included in their software.
Dependencies¶
Development Environment ELT DevEnv¶
The ELT Linux Development Environment (DevEnv) comprises a collection of hardware, software procedures and tools for the developing, testing and debugging of software components for the ELT. It has to support large-scale and long-term maintenance of software.
Further information regarding the ELT Development Environment can be found here:
Deployment¶
The ELT standard tools for deployment (which is the action of activating or deactivating software
processes on remote server hardware) will be based on Nomad and Consul. Once these tools
are readily integrated into the ELT software ecosystem the RTC Toolkit will make use of them.
Until then, the RTC Toolkit uses shell scripts to facilitate deployment in a very simple
way. These scripts prepare the environment and bring up the respective applications with the
required command line arguments. Additionally, shell scripts that use Nomad for deployment
have been added in this release to demonstrate that the toolkit can be deployed using Nomad.
Similarly a fake service discovery mechanism was introduced to provide rudimentary support for name service (see Service Discovery).
Core Integration Infrastructure CII¶
The RTC Toolkit makes use of the CII MAL (Middleware Abstraction Layer) for non-time-critical inter component messaging. The two main mechanisms used are request/reply and publish/subscribe.
In addition this version also supports CII OLDB (Online Database). In the future other CII services will be integrated as well.
Note
To avoid spurious error messages, the CII_LOGS environment variable must be set manually before running any binaries that link to the RTC Toolkit or CII libraries directly.
Explicitly setting the CII_LOGS environment variable is a temporary workaround for ELT Development Environment version 3.6.0. This will likely not be necessary in future versions of the ELT Development Environment.
FastDDS dds¶
FastDDS is an open source implementation of OMG’s Data Distribution Service (DDS) a middleware framework standard for data exchanges using a publish–subscribe pattern. It is used in the RTC Toolkit for reliable multicast telemetry data transfer, in particular between Telemetry Republisher and Telemetry Subscriber components.
FastDDS and tools are provided as part of ELT Development Environment. This version of RTC Toolkit is based on FastDDS version 2.4.0.
Note
In version of ELT Development Environment used fastddsMonitor GUI tool does not work.
To get working version you need to updated it to a newer version as follow (as root):
yum update opt-FastDDS-Monitor
Rapid Application Development rad¶
The rad application framework is an ESO software product that enables the development of
event-driven applications for the ELT. It is based on call-backs or state machines.
At present, the RTC Toolkit mainly uses rad to realise its state machines and internal
event handling. More details rad can be found in its user manual.
Extensible Test Runner etr¶
The RTC Toolkit makes use of the extensible test runner etr for integration testing.
The following features are available:
Run Robot Framework tests with the robot plugin.
Request test resources with the resources plugin.
Modify template files with Jinja2 template engine and the jinja2 plugin.
Deploy software with Nomad with the nomad plugin (experimental support).
For details see the etr User Manual.
Roadrunner¶
Roadrunner is a project containing independent and reusable C++ libraries for high performance applications. RTC Tk uses the shared memory library ipcq and NUMA++ which is a library to help simplify application of NUMA policies. It is essentially a set of APIs to interact with libnuma and certain pthread APIs to control memory policy, CPU affinity and scheduler. For details see the documentation provided for each roadrunner component.