Press Release
The Strange Structures of the Saturn Nebula
27 September 2017
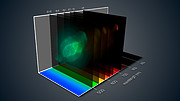
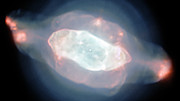
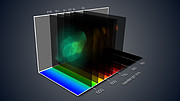
The spectacular planetary nebula NGC 7009, or the Saturn Nebula, emerges from the darkness like a series of oddly-shaped bubbles, lit up in glorious pinks and blues. This colourful image was captured by the powerful MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), as part of a study which mapped the dust inside a planetary nebula for the first time. The map — which reveals a wealth of intricate structures in the dust, including shells, a halo and a curious wave-like feature — will help astronomers understand how planetary nebulae develop their strange shapes and symmetries.
The Saturn Nebula is located approximately 5000 light years away in the constellation of Aquarius (The Water Bearer). Its name derives from its odd shape, which resembles everyone’s favourite ringed planet seen edge-on.
But in fact, planetary nebulae have nothing to do with planets. The Saturn Nebula was originally a low-mass star, which expanded into a red giant at the end of its life and began to shed its outer layers. This material was blown out by strong stellar winds and energised by ultraviolet radiation from the hot stellar core left behind, creating a circumstellar nebula of dust and brightly-coloured hot gas. At the heart of the Saturn Nebula lies the doomed star, visible in this image, which is in the process of becoming a white dwarf [1].
In order to better understand how planetary nebulae are moulded into such odd shapes, an international team of astronomers led by Jeremy Walsh from ESO used the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) to peer inside the dusty veils of the Saturn Nebula. MUSE is an instrument installed on one of the four Unit Telescopes of the Very Large Telescope at ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile. It is so powerful because it doesn’t just create an image, but also gathers information about the spectrum — or range of colours — of the light from the object at each point in the image.
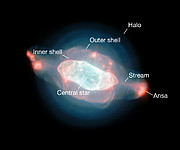
The team used MUSE to produce the first detailed optical maps of the gas and dust distributed throughout a planetary nebula [2]. The resulting image of the Saturn Nebula reveals many intricate structures, including an elliptical inner shell, an outer shell, and a halo. It also shows two previously imaged streams extending from either end of the nebula’s long axis, ending in bright ansae (Latin for “handles”).
Intriguingly, the team also found a wave-like feature in the dust, which is not yet fully understood. Dust is distributed throughout the nebula, but there is a significant drop in the amount of dust at the rim of the inner shell, where it seems that it is being destroyed. There are several potential mechanisms for this destruction. The inner shell is essentially an expanding shock wave, so it may be smashing into the dust grains and obliterating them, or producing an extra heating effect that evaporates the dust.
Mapping the gas and dust structures within planetary nebulae will aid in understanding their role in the lives and deaths of low mass stars, and it will also help astronomers understand how planetary nebulae acquire their strange and complex shapes.
But MUSE’s capabilities extend far beyond planetary nebulae. This sensitive instrument can also study the formation of stars and galaxies in the early Universe, as well as map the dark matter distribution in galaxy clusters in the nearby Universe. MUSE has also created the first 3D map of the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula (eso1518) and imaged a spectacular cosmic crash in a nearby galaxy (eso1437).
Notes
[1] Planetary nebulae are generally short-lived; the Saturn Nebula will last only a few tens of thousands of years before expanding and cooling to such an extent that it becomes invisible to us. The central star will then fade as it becomes a hot white dwarf.
[2] The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has previously provided a spectacular image of the Saturn Nebula — but, unlike MUSE, it cannot reveal the spectrum at each point over the whole nebula.
More information
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world’s most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It is supported by 16 countries: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Czechia, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom, along with the host state of Chile. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its world-leading Very Large Telescope Interferometer as well as two survey telescopes, VISTA working in the infrared and the visible-light VLT Survey Telescope. ESO is also a major partner in two facilities on Chajnantor, APEX and ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. And on Cerro Armazones, close to Paranal, ESO is building the 39-metre Extremely Large Telescope, the ELT, which will become “the world’s biggest eye on the sky”.
Links
- Photos of the VLT
- Photos of MUSE
- Press release on first light of MUSE
Contacts
Jeremy Walsh
ESO
Garching bei München, Germany
Email: jwalsh@eso.org
Richard Hook
ESO Public Information Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6655
Cell: +49 151 1537 3591
Email: rhook@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso1731 |
| Name: | NGC 7009, Saturn Nebula |
| Type: | Milky Way : Nebula : Type : Planetary |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | MUSE |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.