Mitteilung
ALMA erforscht das magnetische Universum
Erste Messungen in allen Polarisationskanälen zeigen die überragenden Polarimetrie-Fähigkeiten von ALMA
19. Juli 2016
Neue Beobachtungen haben bestätigt, dass ALMA durch seine hervorragende Empfindlichkeit und Kalibrationsgenauigkeit zu einem führenden Instrument für polarimetrische Messungen bei Wellenlängen im Millimeter-Bereich wird.
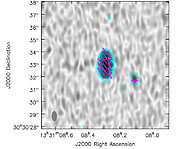
Obwohl ALMA (the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) seit 2011 in Betrieb ist, finden laufend Beobachtungen statt, die die Leistungsstärke des Observatoriums verifizieren. ALMA ist für empfindliche Polarimetrie-Messungen ausgelegt. Dabei wird die Polarisation von Radiowellen untersucht, um die Eigenschaften magnetischer Felder zu untersuchen. Astronomen haben kürzlich über die ersten Beobachtungen zur Aufnahme in allen Polarisationskanälen mit ALMA berichtet, wobei gezeigt wurde, dass ALMA hervorragend für diese Aufgabe geeignet ist.
Für die Beobachtungen haben Astronomen die helle Lichtquelle 3C 286 beobachtet – ein Quasar, der sich in einer Entfernung von etwa 7,3 Milliarden Lichtjahren von uns entfernt befindet. 3C 286 ist eine sehr starke Quelle von Radiowellen und wurde bereits von vielen weiteren Teleskopen beobachtet. Die Radioemission des Objekts ist dafür bekannt, stark polarisiert zu sein. Er ist also ein besonders geeigneter Kandidat, um die Leistungsfähigkeit von ALMA zu testen. Die Beobachtungen enthüllten Details, die bisher nicht erkennbar waren, und zeigen deutlich, dass das magnetische Feld sehr viel stärker und in der inneren Region geordneter ist, als der dem Quasar entweichende Strahl vermuten lässt. Dies hilft den Forschern dabei, die Struktur des magnetischen Felds im Zentrum des Quasars zu verstehen und weitere Erkenntnisse über die Hintergründe des physikalischen Prozesses, die für die Emission der Radiostrahlen verantwortlich sind, herauszufinden.
“Diese Beobachtung hat die große Leistungsfähigkeit der Polarimetrie-Beobachtungen mit ALMA gezeigt”, erklärt Hiroshi Nagai, Leiter des Nachweisteams am National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. “Das ist ein wichtiger Meileinstein für das Projekt.”
Magnetische Felder sind für viele kosmische Gegebenheiten von Relevanz. Sie sind jedoch häufig schwer zu vermessen. Die Polarimetrie ist eine der wenigen Methoden, die ausführlichere Aussagen über die magnetischen Felder zulässt. Die polarisierten Komponenten – die Observable bei der Polarimetrie – betragen lediglich einige wenige Prozent der gesamten Strahlung an Radiowellen eines Objekts. Eine hohe Sensitivität ist deshalb essenziell, um präzise Polarimetrie-Untersuchungen durchzuführen. ALMA weist eine Empfindlichkeit auf, die für diese entscheidenden Polarimetrie-Beobachtungen notwendig sind, wie die aktuelle Studie gezeigt hat.
Weitere Informationen
Die hier präsentierten Ergebnisse von H. Nagai et al. wurden am 20. Juni 2016 im Astrophysical Journal unter dem Titel “ALMA Science Verification Data: Millimeter Continuum Polarimetry of the Bright Radio Quasar 3C 286” publiziert.
Die beteiligten Wissenschaftler sind: H. Nagai (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Tokyo, Japan), K. Nakanishi (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Tokyo, Japan; The Graduate University for Advanced Studies, Tokyo, Japan; Joint ALMA Observatory, Santiago, Chile), R. Paladino (INAF-Osservatorio di Radioastronomia, Bologna, Italien), C.L.H. Hull (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA; Jansky Fellow of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory), P. Cortes (Joint ALMA Observatory, Santiago, Chile; National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA), G. Moellenbrock (National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Socorro, New Mexico, USA), E. Fomalont (Joint ALMA Observatory, Santiago, Chile; National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA), K. Asada (The Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Taipei, Taiwan) und K. Hada (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Tokyo, Japan).
Das Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) ist eine internationale astronomische Einrichtung, die gemeinsam von der ESO, der US-amerikanischen National Science Foundation (NSF) der USA und den japanischen National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) in Kooperation mit der Republik Chile betrieben wird. Getragen wird ALMA von der ESO im Namen ihrer Mitgliedsländer, von der NSF in Zusammenarbeit mit dem kanadischen National Research Council (NRC), dem taiwanesischen National Science Council (NSC) und NINS in Kooperation mit der Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan sowie dem Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
Bei Entwicklung, Aufbau und Betrieb ist die ESO federführend für den europäischen Beitrag, das National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), das seinerseits von Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI) betrieben wird, für den nordamerikanischen Beitrag und das National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) für den ostasiatischen Beitrag. Dem Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) obliegt die übergreifende Projektleitung für den Aufbau, die Inbetriebnahme und den Beobachtungsbetrieb von ALMA.
Kontaktinformationen
Hiroshi Nagai
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
Osawa 2-21-1
Mitaka, Tokyo, Japan
E-Mail: hiroshi.nagai@nao.ac.jp
Peter Grimley
ESO Assistant Public Information Officer
Garching bei München
E-Mail: pgrimley@partner.eso.org
Über die Mitteilung
| ID: | ann16050 |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.