Press Release
Extrasolar Giant Planet in Earth-like Orbit
Discovery from a Long-term Project at La Silla
29 July 1999
A new extrasolar planet has been found at the ESO La Silla Observatory as a companion to iota Horologii (iota Hor). This 5.4-mag solar-type star is located at a distance of 56 light-years and is just visible to the unaided eye in the southern constellation Horologium (The Pendulum Clock).
The discovery is the result of a long-term survey of forty solar-type stars that was begun in November 1992. It is based on highly accurate measurements of stellar radial velocities, i.e. the speed with which a star moves along the line of sight. The presence of a planet in orbit around a star is inferred from observed, regular changes of this velocity, as the host star and its planet revolve around a common center of gravity. Since in all cases the star is much heavier than the planet, the resulting velocity variations of the star are always quite small.
The team that found the new planet, now designated iota Hor b , consists of Martin Kürster , Michael Endl and Sebastian Els (ESO-Chile), Artie P. Hatzes and William D. Cochran (University of Texas, Austin, USA), and Stefan Döbereiner and Konrad Dennerl (Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Garching, Germany).
Iodine cell provides very accurate velocity measurements
iota Hor b represents the first discovery of an extrasolar planet with an ESO instrument [1]. The finding is based on data obtained with ESO's highest-resolution spectrograph, the Coudé Echelle Spectrometer (CES) at the 1.4-m Coudé Auxiliary Telescope (CAT). While this telescope has recently been decommissioned, the CES instrument is now coupled via an optical fiber link to the larger ESO 3.6-m telescope, thus permitting the continuation of this survey.
The high precision radial velocity measurements that are necessary for a study of this type were achieved by means of a special calibration technique. It incorporates an iodine gas absorption cell and sophisticated data modelling.
The cell is used like an optical filter that adds its own absorption features to the absorption line spectrum of the star. When the radial velocity of a star changes, the wavelength of its spectral lines will shift according to the Doppler effect. They are then seen to move, relative to those of the iodine spectrum.
Because of the relative nature of this measurement, the shift and hence the star's velocity change can be measured with a precision that is much higher than what the mechanical/optical stability of the spectrograph would otherwise allow. This particular technique is currently being applied by several research groups in the world and has led to most of the recent extra-solar planet discoveries.
The new planet and its orbit
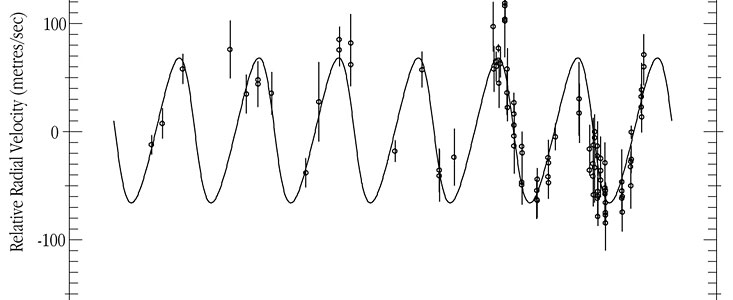
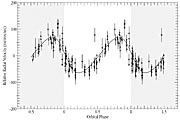
For the star iota Hor , a measurement precision of about ± 17 m/sec (± 61 km/hour) was achieved. This is a very high accuracy in astronomical terms and it enabled the astronomers to detect radial velocity variations with an amplitude of ± 67 m/sec (or 134 m/sec peak-to-peak), cf. eso9938a, eso9938b.
Five and a half years of monitoring and 95 individual spectra with exposure times between 15 and 30 minutes eventually revealed the presence of a planetary companion .
iota Hor b has an orbital period of 320 days. From this period, the known mass of the central star (1.03 solar masses) and the amplitude of the velocity changes, a mass of at least 2.26 times that of planet Jupiter is deduced for the planet.
It revolves around the host star in a somewhat elongated orbit (the eccentricity is 0.16). If it were located in our own solar system, this orbit would stretch from just outside the orbit of Venus (at 117 million km or 0.78 Astronomical Units from the Sun) to just outside the orbit of the Earth (the point farthest from the Sun, at 162 million km or 1.08 Astronomical Units)
The new giant planet is thus moving in an orbit not unlike that of the Earth. In fact, of all the planets discovered so far, the orbit of iota Hor b is the most Earth-like. Also, with a spectral type of G0 V , its host star is quite similar to the Sun (G2 V).
iota Hor b is, however, at least 720 times more massive than the Earth and it is probably more similar to planet Jupiter in our own solar system. While the radial velocity technique described above only determines a minimum value for the planet's mass, an analysis of the velocity with which the star turns around its own axis suggests that the true mass of iota Hor b is unlikely to be much higher.
A difficult case
Natural phenomena with periods near one solar year always present a particular challenge to astronomers. This is one of the reasons why it has been necessary to observe the iota Hor system for such a long time to be absolutely sure about the present result.
First, special care must be taken to verify that the radial velocity variations found in the data are not an artefact of the Earth's movement around the Sun. In any case, the effect of this movement on the measurements must be accurately accounted for; it reaches about ± 30 km/sec over one year, i.e. much larger than the effect of the new planet. In the present case of iota Hor , this was thoroughly tested and any residual influence of the Earth's motion can be excluded.
A second complication arises from the fact that for Earth-bound telescopes, the visibility of a particular star changes in the course of the year. This creates `windows of opportunity', i.e. certain times when a given star can best be observed. That leads to a tendency to observe and re-observe the star when the planet is in the same part of its orbit. The full variation in radial velocity will therefore only be revealed after a sufficiently long time span has elapsed, covering several revolutions of the planet around the central star.
More planets in the iota Hor system?
The comparatively high scatter of the data points from the best fitting radial velocity curve presents an additional puzzle. While the accuracy of these measurements was determined as ± 17 m/sec (for other, similar stars, with and without known planets, an even higher precision of ± 14 m/sec was found with the same instrument), the scatter of the measurements around the mean velocity curve is higher, about ± 27 m/sec. This indicates that the discovered planet cannot be the whole story.
There are two possible explanations for this additional variability.
Either there is a second planet with another period in the same system, or activity on the surface of the star causes slight changes in its spectrum, influencing the velocity measurements.
There are in fact indications that iota Hor is more active than the Sun, hence making the second explanation quite plausible. If so, it appears that the new planet is orbiting around a relatively young star, since such stars are typically more active than older ones like the Sun.
Follow-up observations
One of the next steps during the investigation of iota Hor will therefore be to get clues to its age. In any case, it is important to learn more about the properties of planetary orbits around young stars, in order to improve the theory of star and planet formation.
After an upgrade to a spectral resolution more than twice as high as before, and with the larger light collecting power of the ESO 3.6-m telescope at its disposal, the CES spectrograph is now ready to perform direct measurements of the spectral instabilities that might cause the additional radial velocity variations in iota Hor . This project is high on the list of the discoverers.
However, they will also follow-up the other explanation - a second planet. Longer series of measurements may reveal additional companions in orbits with longer or shorter periods of revolution.
Observations of iota Hor will therefore be continued for several more years. Due to its rather complex radial velocity variations, iota Hor may thus soon become one of the better studied stars in the southern sky.
Notes
[1] Extrasolar Planets are also being found with the 1.2-m Swiss telescope at La Silla. An early success was described in eso9818.
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso9938 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 12/99 |
| Name: | Iota Horologii |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star Milky Way : Star : Circumstellar Material : Planetary System |
| Facility: | Coudé Auxiliary Telescope |
| Instruments: | Coudé Echelle Spectrometer (CES) |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.