Press Release
A Faint and Lonely Brown Dwarf in the Solar Vicinity
Discovery of KELU-1 Promises New Insights into Strange Objects
28 April 1997
Brown Dwarfs are star-like objects which are too small to become real stars, yet too large to be real planets. Their mass is too small to ignite those nuclear processes which are responsible for the large energies and high temperatures of stars, but it is much larger than that of the planets we know in our solar system. Until now, very few Brown Dwarfs have been securely identified as such. Two are members of double-star systems, and a few more are located deep within the Pleiades star cluster. Now, however, Maria Teresa Ruiz of the Astronomy Department at Universidad de Chile (Santiago de Chile), using telescopes at the ESO La Silla observatory, has just discovered one that is all alone and apparently quite near to us. Contrary to the others which are influenced by other objects in their immediate surroundings, this new Brown Dwarf is unaffected and will thus be a perfect object for further investigations that may finally allow us to better understand these very interesting celestial bodies. It has been suggested that Brown Dwarfs may constitute a substantial part of the unseen dark matter in our Galaxy. This discovery may therefore also have important implications for this highly relevant research area.
Searching for nearby faint stars
The story of this discovery goes back to 1987 when Maria Teresa Ruiz decided to embark upon a long-term search (known as the Calan-ESO proper-motion survey) for another type of unusual object, the so-called White Dwarfs, i.e. highly evolved, small and rather faint stars. Although they have masses similar to that of the Sun, such stars are no larger than the Earth and are therefore extremely compact. They are particularly interesting, because they most probably represent the future end point of evolution of our Sun, some billions of years from now.
For this project, the Chilean astronomer obtained large-field photographic exposures with the 1-m ESO Schmidt telescope at La Silla, each covering a sky area of 50.5 x 50.5. When comparing plates of the same sky field obtained at time intervals of several years [1], she was able to detect, among the hundreds of thousands of stellar images on the plates, a few faint ones whose positions had changed a little in the meantime. The search technique is based on the fact that such a shift is a good indicator of the object being relatively nearby. It must therefore also be intrinsically faint, i.e. a potential White Dwarf candidate.
On every pair of plates, approximately twenty faint moving objects were detected with proper motions [2] of more than 0.25 arcsec per year. Indeed, follow-up spectroscopic observations showed that about 20 percent of these or about four per plate were White Dwarfs. Until now, a total of forty new White Dwarfs have been discovered during this very successful project, i.e. over ten times more than originally expected.
And then - a Brown Dwarf!
When checking two plates with a time inverval of 11 years, Maria Teresa Ruiz earlier this year discovered a very faint object in the southern constellation of Hydra (The Water-Snake), moving at 0.35 arcsec per year (cf. ESO Press Photo eso9709). In order to establish its true nature, she obtained its spectrum (in the visual to near-infrared region from wavelengths 450-1000 nm) on March 15 using the ESO 3.6-m telescope and the EFOSC1 spectrograph.
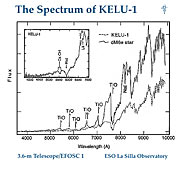
To her great surprise, the spectrum was of a type never seen before and certainly not that of a White Dwarf or any other easily identifiable type of star (cf. ESO Press Photo eso9709). In particular, there were no signs of spectral bands of titanium oxide (TiO) or vanadium oxide (VO) which are common in very cool stars, nor of the spectral lines seen in White Dwarfs. On the other hand, an absorption line of the short-lived element lithium was identified, as well as a hydrogen line in emission.
However, when the colour of this mysterious object was measured in different wavebands, it was found to be very red and quite similar to that of one of the two known Brown Dwarfs in double star systems. The presence of the lithium line in the spectrum is also an indication that it might be of that type.
The astronomer now decided to give the new object the name KELU-1 ; this word means 'red' in the language of the Mapuche people, the ancient population in the central part of Chile. Its visual magnitude is 22.3, i.e. more than 3 million times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye.
In early April, additional infrared observations with the UKIRT (UK Infrared Telescope) on Mauna Kea (Hawaii) by Sandra K. Leggett (Joint Astrophysical Centre, Hilo, Hawaii, USA) confirmed the Brown Dwarf nature of KELU-1, in particular through the unambiguous detection of Methane (CH 4) bands in its spectrum.
The nature of Brown Dwarfs
Brown Dwarfs are first of all characterised by their low mass. When a body of such a small mass is formed in an interstellar cloud and subsequently begins to contract, its temperature at the centre will rise, but it will never reach a level that is sufficient to ignite the nuclear burning of hydrogen to helium, the process that it is main source of energy in the Sun and most other stars. The Brown Dwarf will just continue to contract, more and more slowly, and it will eventually fade from view.
This is also the reason that some astronomers consider Brown Dwarfs in the Milky Way and other galaxies as an important component of the 'dark matter' whose presence is infered from other indirect measurements but has never been directly observed.
It is assumed that the mass limit that separates nuclear-burning stars and slowly contracting Brown Dwarfs is at about 90 times the mass of the giant planet Jupiter, or 8 percent of that of the Sun.
KELU-1: a great opportunity for Brown Dwarf studies
Assuming that KELU-1 is identical to other known Brown Dwarfs, its measured characteristics indicate that it must be located at a distance of only 10 parsecs, that is about 33 light-years, from the solar system. Its temperature is obviously below 1700 degrees C (where TiO and VO condense as dust grains [3] so that the spectral lines of these molecules are no longer seen). Its mass can be no more than 75 times that of Jupiter, or 6 percent of that of the Sun.
During recent years, several Brown Dwarf candidates have been de-masked as low-mass stars and only recently a few Brown Dwarfs were identified in the Pleiades star cluster. Those Brown Dwarfs are quite young and therefore comparatively hotter and brighter.
Contrarily, KELU-1 is most probably somewhat older and its unique location so close to us greatly facilitates future investigations. Moreover, it is not at all 'disturbed' by the presence of other objects in its immediate surroundings, as this is the case for all other known objects of this type.
It will now be important to obtain accurate measurements of KELU-1's parallax, that is, the small annual change of its position in the sky that is caused by the Earth's motion around the Sun and thus the viewing angle of an Earth-based observer. This should be possible within the next year.
Moreover, high resolution spectral investigations with large telescope facilities, soon to include the ESO Very Large Telescope at the Paranal observatory in northern Chile, will now for the first time enable us to investigate the processes that take place in the relatively cold upper layers of Brown Dwarfs. For instance, the observed presence of lithium shows that its atmosphere must be different from that of low-mass stars.
KELU-1 and the 'Dark Matter'
From the fact that KELU-1 is so faint that it was barely detectable on the ESO Schmidt plates, it is possible to estimate that the total volume so far surveyed for this type of objects by this research programme is rather small, only about 23 cubic parsecs (800 cubic light-years). A further consideration of the search statistics indicates that less than 10 percent of the Brown Dwarfs present in the surveyed volume would have been found. This translates into a local density of about 0.4 such objects per cubic parsec.
Although the mass density of Brown Dwarfs derived from this estimate is insufficient to constitute all the 'dark matter' in the Milky Way Galaxy, it is consistent with the most recent estimates of the local mass density, both observed and as infered from dynamical considerations of the motions of stars in the solar neighborhood.
Notes
[1] This is done by means of a so-called blink-comparator , an optical device in which the two plates are placed. A tilting mirror allows to view the same sky field alternately on the two plates. Any celestial object that has changed its position will appear to `jump' back and forth and can thus be identified.
[2] A proper motion in the sky of 0.25 arcsec/year corresponds to a transversal speed of about 12 km/sec if the object is located at a distance of 10 parsec, or 32.6 light-years. The largest known proper motion of an object outside the solar system is that of Barnard's Star at about 10 arcsec/year.
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso9709 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 07/97 |
| Name: | KELU-1 |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Type : Brown Dwarf Milky Way : Star : Grouping : Binary |
| Facility: | ESO 3.6-metre telescope |
| Instruments: | EFOSC |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.