Press Release
Astronomers Find First Earth-like Planet in Habitable Zone
The Dwarf Carried Other Worlds Too!
25 April 2007
Astronomers have discovered the most Earth-like planet outside our Solar System to date, an exoplanet with a radius only 50% larger than the Earth and capable of having liquid water. Using the ESO 3.6-m telescope, a team of Swiss, French and Portuguese scientists discovered a super-Earth about 5 times the mass of the Earth that orbits a red dwarf, already known to harbour a Neptune-mass planet. The astronomers have also strong evidence for the presence of a third planet with a mass about 8 Earth masses.
This exoplanet - as astronomers call planets around a star other than the Sun - is the smallest ever found up to now [1] and it completes a full orbit in 13 days. It is 14 times closer to its star than the Earth is from the Sun. However, given that its host star, the red dwarf Gliese 581 [2], is smaller and colder than the Sun - and thus less luminous - the planet nevertheless lies in the habitable zone, the region around a star where water could be liquid! The planet's name is Gliese 581 c.
"We have estimated that the mean temperature of this super-Earth lies between 0 and 40 degrees Celsius, and water would thus be liquid," explains Stéphane Udry, from the Geneva Observatory (Switzerland) and lead-author of the paper reporting the result. "Moreover, its radius should be only 1.5 times the Earth's radius, and models predict that the planet should be either rocky - like our Earth - or fully covered with oceans," he adds.
"Liquid water is critical to life as we know it," avows Xavier Delfosse, a member of the team from Grenoble University (France). "Because of its temperature and relative proximity, this planet will most probably be a very important target of the future space missions dedicated to the search for extra-terrestrial life. On the treasure map of the Universe, one would be tempted to mark this planet with an X."
The host star, Gliese 581, is among the 100 closest stars to us, located only 20.5 light-years away in the constellation Libra ("the Scales"). It has a mass of only one third the mass of the Sun. Such red dwarfs are intrinsically at least 50 times fainter than the Sun and are the most common stars in our Galaxy: among the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 belong to this class.
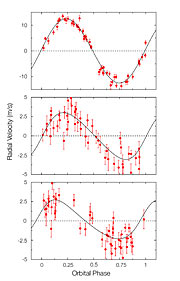
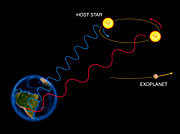
"Red dwarfs are ideal targets for the search for low-mass planets where water could be liquid. Because such dwarfs emit less light, the habitable zone is much closer to them than it is around the Sun," emphasizes Xavier Bonfils, a co-worker from Lisbon University. Planets lying in this zone are then more easily detected with the radial-velocity method [3], the most successful in detecting exoplanets.
Two years ago, the same team of astronomers already found a planet around Gliese 581 (see ESO Press Release eso0539). With a mass of 15 Earth-masses, i.e. similar to that of Neptune, it orbits its host star in 5.4 days. At the time, the astronomers had already seen hints of another planet. They therefore obtained a new set of measurements and found the new super-Earth, but also clear indications for another one, an 8 Earth-mass planet completing an orbit in 84 days. The planetary system surrounding Gliese 581 contains thus no fewer than 3 planets of 15 Earth masses or less, and as such is a quite remarkable system.
The discovery was made thanks to HARPS (High Accuracy Radial Velocity for Planetary Searcher), perhaps the most precise spectrograph in the world. Located on the ESO 3.6-m telescope at La Silla, Chile, HARPS is able to measure velocities with a precision better than one metre per second (or 3.6 km/h)! HARPS is one of the most successful instruments for detecting exoplanets and holds already several recent records, including the discovery of another 'Trio of Neptunes' (ESO Press Release eso0618, see also ESO Press Release eso0427).
The detected velocity variations are between 2 and 3 metres per second, corresponding to about 9 km/h! That's the speed of a person walking briskly. Such tiny signals could not have been distinguished from 'simple noise' by most of today's available spectrographs.
"HARPS is a unique planet hunting machine," says Michel Mayor, from Geneva Observatory, and HARPS Principal Investigator. "Given the incredible precision of HARPS, we have focused our effort on low-mass planets. And we can say without doubt that HARPS has been very successful: out of the 13 known planets with a mass below 20 Earth masses, 11 were discovered with HARPS!"
HARPS is also very efficient in finding planetary systems, where tiny signals have to be uncovered. The two systems known to have three low mass planets - HD 69830 and Gl 581 - were discovered by HARPS.
"And we are confident that, given the results obtained so far, finding a planet with the mass of the Earth around a red dwarf is within reach," affirms Mayor.
Notes
[1]: Using the radial velocity method, astronomers can only obtain a minimum mass (as it is multiplied by the sine of the inclination of the orbital plane to the line of sight, which is unknown). From a statistical point of view, this is however often close to the real mass of the system. Two other systems have a mass close to this. The icy planet around OGLE-2005-BLG-390L, discovered by microlensing with a network of telescopes including one at La Silla (ESO 03/06), has a (real) mass of 5.5 Earth masses. It, however, orbits much farther from its small host star than the present one and is hence much colder. The other is one of the planets surrounding the star Gliese 876. It has a minimum mass of 5.89 Earth masses (and a probable real mass of 7.53 Earth masses) and completes an orbit in less than 2 days, making it too hot for liquid water to be present.
[2]: Gl 581, or Gliese 581, is the 581th entry in the Gliese Catalogue, which lists all known stars within 25 parsecs (81.5 light years) of the Sun. It was originally compiled by Gliese and published in 1969, and later updated by Gliese and Jahreiss in 1991.
[3]: This fundamental observational method is based on the detection of variations in the velocity of the central star, due to the changing direction of the gravitational pull from an (unseen) exoplanet as it orbits the star. The evaluation of the measured velocity variations allows deducing the planet's orbit, in particular the period and the distance from the star, as well as a minimum mass.
More information
This research is reported in a paper submitted as a Letter to the Editor of Astronomy and Astrophysics ("The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets : XI. An habitable super-Earth (5 MEarth) in a 3-planet system", by S. Udry et al.) The paper is available from http://obswww.unige.ch/~udry/udry_preprint.pdf.
The team is composed of Stéphane Udry, Michel Mayor, Christophe Lovis, Francesco Pepe, and Didier Queloz (Geneva Observatory, Switzerland), Xavier Bonfils (Lisbonne Observatory, Portugal), Xavier Delfosse, Thierry Forveille, and C.Perrier (LAOG, Grenoble, France), François Bouchy (Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, France), and Jean-Luc Bertaux (Service d'Aéronomie du CNRS, France)
Contacts
Stéphane Udry
Observatory of Geneva University
Geneva, Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 379 22 00
Email: Stephane.Udry@obs.unige.ch
Michel Mayor
Observatory of Geneva University
Geneva, Switzerland
Email: Michel.Mayor@obs.unige.ch
Xavier Delfosse
LAOG
France
Tel: +33 476 51 42 06
Email: Xavier.Delfosse@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr
Thierry Forveille
LAOG
France
Email: Thierry.Forveille@obs.ujf-grenoble.fr
Xavier Bonfils
Lisbonne Observatory
Lisbonne, Portugal
Tel: +351 21 361 67 43
Email: xavier.bonfils@oal.ul.pt
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0722 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 22/07 |
| Name: | Exoplanets, Gliese 581, Gliese 581 c |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Circumstellar Material : Planetary System |
| Facility: | ESO 3.6-metre telescope |
| Instruments: | HARPS |
| Science data: | 2007A&A...469L..43U |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.