Press Release
It's Far, It's Small, It's Cool: It's an Icy Exoplanet!
Distant Planet Brings Astronomers Closer To Home
25 January 2006
Using a network of telescopes scattered across the globe, including the Danish 1.54m telescope at ESO La Silla (Chile), astronomers [1] discovered a new extrasolar planet significantly more Earth-like than any other planet found so far. The planet, which is only about 5 times as massive as the Earth, circles its parent star in about 10 years. It is the least massive exoplanet around an ordinary star detected so far and also the coolest [2]. The planet most certainly has a rocky/icy surface. Its discovery marks a groundbreaking result in the search for planets that support life.
The new planet, designated by the unglamorous identifier of OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb, orbits a red star five times less massive than the Sun and located at a distance of about 20,000 light years, not far from the centre of our Milky Way galaxy.
Its relatively cool parent star and large orbit implies that the likely surface temperature of the planet is 220 degrees Centigrade below zero, too cold for liquid water. It is likely to have a thin atmosphere, like the Earth, but its rocky surface is probably deeply buried beneath frozen oceans. It may therefore more closely resemble a more massive version of Pluto, rather than the rocky inner planets like Earth and Venus.
"This planet is actually the first and only planet that has been discovered so far that is in agreement with the theories for how our Solar System formed ", said Uffe Gråe Jørgensen (Niels Bohr Institute, Copenhagen, Denmark), member of the team.
The favoured theoretical explanation for the formation of planetary systems proposes that solid 'planetesimals' accumulate to build up planetary cores, which then accrete nebular gas - to form giant planets - if they are sufficiently massive. Around red dwarfs, the most common stars of our Galaxy, this model favours the formation of Earth- to Neptune-mass planets being between 1 and 10 times the Earth-Sun distance away from their host.
"OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb is only the third extra-solar planet discovered so far through microlensing searches ", said Jean-Philippe Beaulieu (Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, France), the lead author. "While the other two microlensing planets have masses of a few times that of Jupiter, the discovery of a 5 Earth mass planet - though much harder to detect than more massive ones - is a strong hint that these lower-mass objects are very common. "
Contrary to most exoplanets discovered, OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb was indeed found using the 'microlensing' technique, based on an effect noted by Albert Einstein in 1912.
"With this method, we let the gravity of a dim, intervening star act as a giant natural telescope for us, magnifying a more distant star, which then temporarily looks brighter ", explained team member Andrew Williams (Perth Observatory, Australia). "A small 'defect' in the brightening reveals the existence of a planet around the lens star. We don't see the planet, or even the star that it's orbiting, we just see the effect of their gravity. "
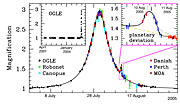
Such an intervening star causes a characteristic brightening that lasts about a month. Any planets orbiting this star can produce an additional signal, lasting days for giant planets down to hours for Earth-mass planets.
In order to be able to catch and characterize these planets, nearly-continuous round-the-clock high-precision monitoring of ongoing microlensing events is required. This is achieved by the PLANET network of 1m-class telescopes consisting of the ESO 1.54m Danish at La Silla (Chile), the Canopus Observatory 1.0m (Hobart, Tasmania, Australia), the Perth 0.6m (Bickley, Western Australia), the Boyden 1.5m (South Africa), and the SAAO 1.0m (Sutherland, South Africa). Since 2005, PLANET operates a common campaign with RoboNet, a UK operated network of 2m fully robotic telescopes currently comprising the Liverpool Telescope (Roque de Los Muchachos, La Palma, Spain) and the Faulkes Telescope North (Haleakala, Hawaii, USA).
The OGLE (Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment) search team (led by A. Udalski, Warsaw University Observatory, Poland) discovered the event OGLE-2005-BLG-390 on 11 July 2005, triggering the PLANET telescopes to start taking data. A light curve consistent with a single lens star peaking at an amplification of about 3 on 31 July 2005 was observed, until 10 August when PLANET member Pascal Fouqué, observing at the Danish 1.54m at ESO La Silla, noticed a planetary deviation. An OGLE point from the same night showed the same trend, while the last half of the planetary deviation, lasting about a day, had been covered by images from Perth Observatory. The MOA (Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics) collaboration was later able to identify the source star on its images and confirmed the deviation.
No other interpretation than the presented sub-Neptune mass planet with its quoted parameters appeared to fit the extensive data set. This discovery brings a fresh look at the field of planetary science.
In particular, astronomers now think that such frozen worlds are much more common than their larger, Jupiter-like brethren. "Indeed if Jupiter-like planets were as widespread, the microlensing method should have found dozens of them by now ", said David Bennett (University of Notre Dame, USA), another PLANET team member.
The microlensing technique is most probably the only method currently capable of detecting planets similar to Earth. "The search for a second Earth is the driving force behind our research and this discovery constitutes a major leap forward since it is the most Earth-like planet we know of so far ", said co-author Daniel Kubas, from ESO.
A report has been published in the 26 January 2006 edition of the leading journal Nature ("Discovery of a cool planet of 5.5 Earth masses through gravitational microlensing" by J.-P. Beaulieu, D. P. Bennett, P. Fouqué, A. Williams, M. Dominik, U. G. Jørgensen, D. Kubas et al.).
High resolution images and their captions are available on this page. This press release is also accompanied by Broadcast quality material.
Notes
[1] This result is a joint effort of three independent microlensing campaigns: PLANET/RoboNet, OGLE, and MOA, involving a total of 73 collaborators affiliated with 32 institutions in 12 countries (France, United Kingdom, Poland, Denmark, Germany, Austria, Chile, Australia, New Zealand, United States of America, South Africa, and Japan).
[2] This value is uncertain by a factor of two. The lowest-mass exoplanet known until now was GJ 876d, which has a probable mass of 7.5 Earth's masses. Unlike the present discovered planet, GJ 876d circles its parent star in about 2 days. It is thus very hot. By comparison, Uranus has about 15 times the mass of the Earth and Neptune, 17, while giant Jupiter weighs as much as 318 earths.
Contacts
Jean-Philippe Beaulieu
Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris
Paris, France
Tel: +33-1-4432-8119
Cell: +33-6-0398-7311
Email: beaulieu@iap.fr
Martin Dominik
University of St Andrews
Fife, UK
Tel: +44-1334-463066
Cell: +44-7753-388787
Email: md35@st-andrews.ac.uk
Daniel Kubas
ESO
Chile
Tel: +49-173-899-3195
Email: dkubas@eso.org
Andrew Williams
Perth Observatory
Perth, Australia
Tel: +61-8-9293-8255
Email: andrew@physics.uwa.edu.au
Joachim Wambsganss
Zentrum für Astronomie der Universitüt Heidelberg
Heidelberg, Germany
Tel: +49-6221-54-1800
Cell: +49-177-419-1800
Email: jkw@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
Pascal Fouqué
Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées
Pyrénées, France
Tel: +33-5-6133-2786
Email: pascal.fouque@ast.obs-mip.fr
Uffe G. Jørgensen
Niels Bohr Institutet Astronomisk Observatorium
Denmark
Tel: +45-35-32-5998
Email: uffegj@nbi.dk
David P. Bennett
University of Notre Dame
Notre Dame, USA
Tel: +1-574-631-8298
Cell: +1-574-315-6621
Email: bennett@nd.edu
Andrzej Udalski
Warsaw University Observatory
Warsaw, Poland
Tel: +48-22-553 05 07
Email: udalski@astrouw.edu.pl
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0603 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 03/06 |
| Name: | OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb |
| Type: | Milky Way : Planet : Type : Terrestrial Milky Way : Star : Circumstellar Material : Planetary System |
| Facility: | Danish 1.54-metre telescope |
| Science data: | 2006Natur.439..437B |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.