Press Release
Nearest Cosmic Mirage
Discovery of quadruply lensed quasar with Einstein ring
16 July 2003
Using the ESO 3.6-m telescope at La Silla (Chile), an international team of astronomers [1] has discovered a complex cosmic mirage in the southern constellation Crater (The Cup). This "gravitational lens" system consists of (at least) four images of the same quasar as well as a ring-shaped image of the galaxy in which the quasar resides - known as an "Einstein ring." The more nearby lensing galaxy that causes this intriguing optical illusion is also well visible. The team obtained spectra of these objects with the new EMMI camera mounted on the ESO 3.5-m New Technology Telescope (NTT), also at the La Silla observatory. They find that the lensed quasar [2] is located at a distance of 6,300 million light-years (its "redshift" is z = 0.66 [3]) while the lensing elliptical galaxy is rougly halfway between the quasar and us, at a distance of 3,500 million light-years (z = 0.3). The system has been designated RXS J1131-1231 - it is the closest gravitationally lensed quasar discovered so far.
Cosmic mirages
The physical principle behind a "gravitational lens" (also known as a "cosmic mirage") has been known since 1916 as a consequence of Albert Einstein's Theory of General Relativity . The gravitational field of a massive object curves the local geometry of the Universe, so light rays passing close to the object are bent (like a "straight line" on the surface of the Earth is necessarily curved because of the curvature of the Earth's surface).
This effect was first observed by astronomers in 1919 during a total solar eclipse. Accurate positional measurements of stars seen in the dark sky near the eclipsed Sun indicated an apparent displacement in the direction opposite to the Sun, about as much as predicted by Einstein's theory. The effect is due to the gravitational attraction of the stellar photons when they pass near the Sun on their way to us. This was a direct confirmation of an entirely new phenomenon and it represented a milestone in physics.
In the 1930's, astronomer Fritz Zwicky (1898 - 1974), of Swiss nationality and working at the Mount Wilson Observatory in California, realised that the same effect may also happen far out in space where galaxies and large galaxy clusters may be sufficiently compact and massive to bend the light from even more distant objects. However, it was only five decades later, in 1979, that his ideas were observationally confirmed when the first example of a cosmic mirage was discovered (as two images of the same distant quasar).
Cosmic mirages are generally seen as multiple images of a single quasar [2], lensed by a galaxy located between the quasar and us. The number and the shape of the images of the quasar depends on the relative positions of the quasar, the lensing galaxy and us. Moreover, if the alignment were perfect, we would also see a ring-shaped image around the lensing object. Such "Einstein rings" are very rare, though, and have only been observed in a very few cases.
Another particular interest of the gravitational lensing effect is that it may not only result in double or multiple images of the same object, but also that the brightness of these images increase significantly, just as it happens with an ordinary optical lens. Distant galaxies and galaxy clusters may thereby act as "natural telescopes" which allow us to observe more distant objects that would otherwise have been too faint to be detected with currently available astronomical telescopes.
Image sharpening techniques resolve the cosmic mirage better
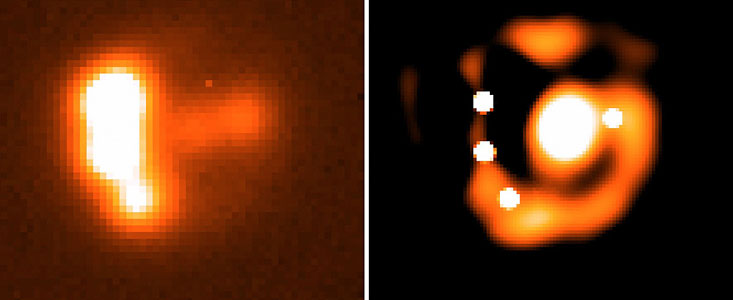
A new gravitational lens, designated RXS J1131-1231, was serendipitously discovered in May 2002 by Dominique Sluse, then a PhD student at ESO in Chile, while inspecting quasar images taken with the ESO 3.6-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory. The discovery of this system profited from the good observational conditions prevailing at the time of the observations. From a simple visual inspection of these images, Sluse provisionally concluded that the system had four star-like (the lensed quasar images) and one diffuse (the lensing galaxy) component.
Because of the very small separation between the components, of the order of one arcsecond or less, and the unavoidable "blurring" effect caused by turbulence in the terrestrial atmosphere ("seeing"), the astronomers used sophisticated image-sharpening software to produce higher-resolution images on which precise brightness and positional measurements could then be performed. This so-called "deconvolution" technique makes it possible to visualize this complex system much better and, in particular, to confirm and render more conspicuous the associated Einstein ring, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0321.
Identification of the source and of the lens
The team of astronomers [1] then used the ESO 3.5-m New Technology Telescope (NTT) at La Silla to obtain spectra of the individual image components of this lensing system. This is imperative because, like human fingerprints, the spectra allow unambiguous identification of the observed objects.
Nevertheless, this is not an easy task because the different images of the cosmic mirage are located very close to each other in the sky and the best possible conditions are needed to obtain clean and well separated spectra. However, the excellent optical quality of the NTT combined with reasonably good seeing conditions (about 0.7 arcsecond) enabled the astronomers to detect the "spectral fingerprints" of both the source and the object acting as a lens.
The evaluation of the spectra showed that the background source is a quasar with a redshift of z = 0.66 [3], corresponding to a distance of about 6,300 million light-years. The light from this quasar is lensed by a massive elliptical galaxy with a redshift z=0.3, i.e. at a distance of 3,500 million light-years or about halfway between the quasar and us. It is the nearest gravitationally lensed quasar known to date .
Because of the specific geometry of the lens and the position of the lensing galaxy, it is possible to show that the light from the extended galaxy in which the quasar is located should also be lensed and become visible as a ring-shaped image. That this is indeed the case is demonstrated by ESO Press Photo eso0321 which clearly shows the presence of such an "Einstein ring", surrounding the image of the more nearby lensing galaxy.
Micro lensing within macro lensing?
The particular configuration of the individual lensed images observed in this system has enabled the astronomers to produce a detailed model of the system. From this, they can then make predictions about the relative brightness of the various lensed images.
Somewhat unexpectedly, they found that the predicted brightnesses of the three brightest star-like images of the quasar are not in agreement with the observed ones - one of them turns out to be one magnitude (that is, a factor of 2.5) brighter than expected . This prediction does not call into question General Relativity but suggests that another effect is at work in this system.
The hypothesis advanced by the team is that one of the images is subject to "microlensing" . This effect is of the same nature as the cosmic mirage - multiple amplified images of the object are formed - but in this case, additional light-ray deflection is caused by a single star (or several stars) within the lensing galaxy. The result is that there are additional (unresolved) images of the quasar within one of the macro-lensed images.
The outcome is an "over-amplification" of this particular image. Whether this is really so will soon be tested by means of new observations of this gravitational lens system with the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT) at Paranal (Chile) and also with the Very Large Array (VLA) radio observatory in New Mexico (USA).
Outlook
Until now, 62 multiple-imaged quasars have been discovered, in most cases showing 2 or 4 images of the same quasar. The presence of elongated images of the quasar and, in particular, of ring-like images is often observed at radio wavelengths. However, this remains a rare phenomenon in the optical domain - only four such systems have been imaged by optical/infrared telecopes until now.
The complex and comparatively bright system RXS J1131-1231 now discovered is a unique astrophysical laboratory . Its rare characteristics (e.g., brightness, presence of a ring-shaped image, small redshift, X-ray and radio emission, visible lens,...) will now enable the astronomers to study the properties of the lensing galaxy, including its stellar content, structure and mass distribution in great detail, and to probe the source morphology. These studies will use new observations which are currently being obtained with the VLT at Paranal, with the VLA radio interferometer in New Mexico and with the Hubble Space Telescope.
Notes
[1] The team consists of Dominique Sluse, Damien Hutsemékers, and Thodori Nakos (ESO and Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique de l'Université de Liège - IAGL), Jean-François Claeskens, Frédéric Courbin, Christophe Jean, and Jean Surdej (IAGL), Malvina Billeres (ESO), and Sergiy Khmil (Astronomical Observatory of Shevchentko University).
[2] Quasars are particularly active galaxies, the centres of which emit prodigious amounts of energy and energetic particles. It is believed that they harbour a massive black hole at their centre and that the energy is produced when surrounding matter falls into this black hole. This type of object was first discovered in 1963 by the Dutch-American astronomer Maarten Schmidt at the Palomar Observatory (California, USA) and the name refers to their "star-like" appearance on the images obtained at that time.
[3] In astronomy, the "redshift" denotes the fraction by which the lines in the spectrum of an object are shifted towards longer wavelengths. Since the redshift of a cosmological object increases with distance, the observed redshift of a remote galaxy also provides an estimate of its distance.
More information
The research described in this press release is presented in a Letter to the Editor, soon to appear in the European professional journal Astronomy & Astrophysics ("A quadruply imaged quasar with an optical Einstein ring candidate : 1RXS J113155.4-123155", by Dominique Sluse et al.).
More information on gravitational lensing and on this research group can also be found at the URL : http://www.astro.ulg.ac.be/GRech/AEOS/.
Contacts
Dominique Sluse
Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique, Université de Liège
Liege, Belgium
Tel: +32 (0)4 366 9761
Email: sluse@astro.ulg.ac.be
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0321 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 19/03 |
| Name: | RXS J1131-1231 |
| Type: | Early Universe : Galaxy : Type : Gravitationally Lensed |
| Facility: | ESO 3.6-metre telescope, New Technology Telescope |
| Instruments: | EFOSC2, EMMI |
| Science data: | 2003A&A...406L..43S |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.