Press Release
How to Become a Star
ESO Telescopes Provide Most Detailed View Ever Into a Dark Cloud
10 January 2001
How do stars like our Sun come into being? Which fundamental processes are responsible for transforming a dark and diffuse interstellar cloud of gas and dust into a much denser, shining object? Astronomers have just taken an important step towards answering this fundamental question. Based on the most detailed study ever made of the internal structure of a small interstellar cloud, three scientists from ESO and the USA [1] have found that it is apparently on the verge of becoming unstable - and thus in the stage immediately preceding a dramatic collapse into a dense and hot, low-mass star.
Interestingly, the current structure of this cloud, a "Bok globule" known as Barnard 68 (B68) [2], is governed by the same basic physics as is that of a star. The cloud is obviously in a temporary state of near-equilibrium, where the inward force of gravity caused by its mass more or less balances that of the outward pressure due to its temperature. But this situation may not last long.
The astronomers believe that this particular cloud, together with some others in the same galactic neighbourhood, constitute the few resistent remains of a much larger cloud that has disappeared due to the influence of strong stellar winds and ultraviolet radiation from young and heavy stars as well as supernova explosions.
The new and unique insight into the pre-collapse phase of the complicated process of stellar birth is based on observations made with ESO telescopes at the La Silla and Paranal observatories in Chile.
From Dark Clouds to Stars
Astronomers have known for some time that stars like our Sun are formed from interstellar clouds of gas and dust. When they contract, the interior temperature rises. If the cloud is sufficiently heavy, it will become so hot at the centre that energy-producing nuclear processes ignite. After a while, the central regions of the cloud reach equilibrium and a new star is born.
Planets are formed from condensations in the surrounding material as this collects in a circumstellar disk.
A good understanding of the origin of stars and planetary systems, like our own solar system, is therefore intimately connected to a detailed knowledge about the conditions in the cold interiors of dark clouds in interstellar space. However, such clouds are highly opaque and their physical structure has remained a mystery for as long as we have known about their existence. The following phases of stellar evolution are much better known and some scientists therefore refer to these very earliest stages as the "missing link" in our current picture of star formation.
Finely balanced equilibrium
The present results are changing this situation. By means of a new and straightforward observational technique, it has now been possible to explore the detailed structure of a nearby cloud. It is found to be quite simple, with the mean density steadily increasing towards the centre. In fact, the way this happens (referred to as the cloud's "density profile") is exactly as expected in an isolated gas sphere at a certain temperature in which the inward force of gravity is finely balanced against the internal thermal pressure.
With this clear physical description it is now possible to determine with unprecedented precision (approx. 3%) the fundamental parameters of the cloud, such as its distance and gas-to-dust ratio.
ESO astronomer João Alves from the team is content: "These measurements constitute a major breakthrough in the understanding of dark clouds. For the first time, the internal structure of a dark cloud has been specified with a detail approaching that which characterizes our knowledge of stellar interiors".
Seeing light through the dark
The observational technique that has led to the new result is straightforward but rather difficult to apply to dark clouds.
It is based on measurements of the light from stars that are located behind the cloud. When this light passes through the cloud, it is absorbed and scattered by the dust inside. The effect depends on the colour (wavelength) and the background stars will appear redder than they really are. It is also proportional to the amount of obscuring material and is therefore largest for stars that are situated behind the cloud's centre.
By measuring the degree of this "reddening" experienced by stars seen through different areas of the cloud, it is thus possible to chart the distribution of dust in the cloud. The finer the net of background stars is, the more detailed this map will be and the better the information about the internal structure of the cloud.
And that is exactly the problem. Even small clouds are so opaque that very few background stars can be seen through them. Only large telescopes and extremely sensitive instruments are able to observe a sufficient number of stars in order to produce significant results. In particular, until now it has never been possible to map the densest, central areas of a dark cloud.
The structure of Barnard 68
At a distance of only 410 light-years, Barnard 68 is one of the nearest dark clouds. Its size is about 12,500 AU (= 2 million million km; 1 Astronomical Unit [AU] = 150 million km), or just about the same as the so-called "Oort Cloud" of long-period comets that surrounds the solar system. The temperature of Barnard 68 is 16 Kelvin (-257 °C) and the pressure at its boundary is 0.0025 nPa, or about 10 times higher than in the interstellar medium (but still 40,000 million million times less than the atmospheric pressure at the Earth's surface!). The total mass of the cloud is about twice that of the Sun.
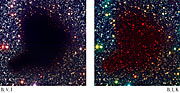
A new investigation of Barnard 68 was carried out by means of instruments at the 3.58-m New Technology Telescope (NTT) at La Silla and the Very Large Telescope (VLT) at Paranal. Long exposures revealed a total of about 3700 background stars (of which over 1000 can only be seen at infrared wavelengths).
Careful measurements of the colours of these stars and hence, the degree of obscuration, allowed the most finely sampled (in more than 1000 individual areas) and most accurate mapping of the dust distribution inside a dark cloud ever performed. In order to further increase the accuracy, the mean dust density was measured in concentric circles around the centre - this resulted in a very accurate determination of the change in dust density with the distance from the centre.
It was found that this dependance is almost exactly as that predicted for a sphere in which the opposite forces of gravity and internal pressure closely balance each other. Nevertheless, it is also evident that Barnard 68 is only marginally stable and is on the verge of collapse.
The origin of Barnard 68
This first-ever, detailed characterization of a dark interstellar cloud that is currently in the stage immediately preceding collapse and subsequent star formation constitutes a very important step towards a better understanding of earliest phases of the stellar life cycle.
The astronomers suggest that Barnard 68 (and its neighbouring brethren, the dark clouds Barnard 69, 70 and 72) may be the precursors of an isolated and sparsely populated association of low-mass solar-like stars. However, where did these clouds come from?
João Alves thinks he and his colleagues know the answer: "It is most likely that they are the remnant cores of particularly resistent parts of a larger cloud. By now, most of it has been 'eaten away' because of strong attrition caused by ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from hot massive stars or 'storms' from exploding supernovae". He adds: "Our new observations show that objects with just the right mass like Barnard 68 can reach a temporary equilibrium and survive for some time before they begin to collapse".
The team is now eager to continue this type of investigation on other dark clouds.
Notes
[1] The team consists of João F. Alves (ESO-Garching, Germany), Charles J. Lada (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, Mass. USA) and Elizabeth A. Lada (University of Florida, Gainsville, Fl., USA).
[2] The Dutch astronomer Bart Bok (1906-1983) studied the dark clouds in the Milky Way and described the small, compact ones as "globules". The early stages of the present investigation of Barnard 68 were presented in ESO PR Photos 29a-c/99, with more background information about this cloud.
More information
The research described in this Press Release is reported in a research article ("Seeing Light Through the Dark: Measuring the Internal Structure of a Cold Dark Cloud"), that appears in the international research jounal Nature on Thursday, January 11, 2001.
Technical information about the photos
ESO Press Photo eso0102a of the sky area of Barnard 68 is based on three frames through B- (440 nm = 0.44 µm - here rendered as blue), V- (0.55 µm - green) and I-band 0.90 µm - red) optical filters, as obtained with the FORS1 instrument at the VLT ANTU telescope on March 27, 1999. The field measures 6.8 x 6.8 arcmin2 (2048 x 2048 pixel2 at 0.20 arcsec/pixel). ESO Press Photo eso0102b is a false-colour composite based on B- (wavelength 0.44 µm - 1.5 min; here rendered as blue), I- (wavelength 0.85 µm - 1.5 min; green), and Ks-filters (2.16 µm - 30 min; red), respectively. The B and I images were obtained on March 1999, with the FORS1 instrument at the 8.2-m VLT ANTU. The Ks image was obtained in March 1999 with the SOFI instrument at the ESO 3.58-m New Technology Telescope (NTT) at La Silla. The sky field measures about 4.9 x 4.9 arcmin2 (1024 x 1024 pixel2 at 0.29 arcsec/pixel). North is up and East is left. ESO Press Photo eso0102c allows a direct comparison between the two views.
Contacts
João F. Alves
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49-89-32006503
Email: jalves@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0102 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 01/01 |
| Name: | B 68, Barnard 68 |
| Type: | Milky Way : Nebula : Appearance : Dark : Bok Globule |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | FORS1 |
| Science data: | 2001Natur.409..159A |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.