Press Release
Cannibal Stars Cause Giant Explosions in Fornax Cluster Galaxy
The VLT Observes Most Remote Novae Ever Seen
28 July 2000
About 70 million years ago, when dinosaurs were still walking on the Earth, a series of violent thermo-nuclear explosions took place in a distant galaxy. After a very long travel across vast reaches of virtually empty space (70 million light-years, or ~ 7 x 10 20 km), dim light carrying the message about these events has finally reached us. It was recorded by the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT) at the Paranal Observatory (Chile) during an observing programme by a group of Italian astronomers [1]. The subsequent analysis has shown that the observers witnessed the most distant nova outbursts ever seen. They were caused by "stellar cannibalism" in binary systems in which one relatively cool star loses matter to its smaller and hotter companion. An instability results that leads to the ignition of a "hydrogen bomb" on the surface of the receiving star.
The "Stella Nova" Phenomenon
A stellar outburst of the type now observed with the VLT is referred to as a "Stella Nova" ("new star" in Latin), or just "Nova" . Novae caused by explosions in binary stars in our home galaxy, the Milky Way system, are relatively frequent and about every second or third year one of them is bright enough to be easily visible with the naked eye. For our ancestors, who had no means to see the faint binary star before the explosion, it looked as if a new star had been born in the sky, hence the name.
The most common nova explosion occurs in a binary stellar system in which a white dwarf (a very dense and hot, compact star with a mass comparable to that of the Sun and a size like the Earth) accretes hydrogen from a cooler and larger red dwarf star [2].
As the hydrogen collects on the surface of the white dwarf star, it becomes progressively hotter until a thermonuclear explosion is ignited at the bottom of the collected gas. A huge amount of energy is released and causes a million-fold increase in the brightness of the binary system within a few hours. After reaching maximum light within some days or weeks, it begins to fade as the hydrogen supply is exhausted and blown into space. The processed material is ejected at high speeds, up to ~1000 km/sec, and may later be visible as an expanding shell of emitting gas.
Altogether, the tremendous flash of light involves the release of about 10 45 ergs in a few weeks, or about as much energy as our Sun produces in 10,000 years.
Supernovae explosions that completely destroy heavier stars at the end of their lives are even more powerful. However, in contrast to supernovae and despite the colossal energy production, the progenitor of a nova is not destroyed during the explosion. Some time after an outburst, transfer of hydrogen from the companion star begins anew, and the process repeats itself with explosions taking place about once every 100,000 years.
The nova star will finally die of "old age" when the cool companion has been completely cannibalized.
Novae as Distance Indicators
Due to their exceptional luminosity, novae can be used as powerful beacons that allow relative distances to different types of galaxies to be measured. The measurement is based on the assumption that novae of the same type are intrinsically equally bright, together with the physical law that states that an object's observed brightness decreases with the square of the distance to the observer.
Thus, if we observe that a nova in a certain galaxy is one million times fainter than a nearby one, we know that it must be one thousand times more distant. In addition, observations of novae in other galaxies shed light on the history of formation of their stars.
Despite their scientific importance, surveys of novae in distant, rich clusters of galaxies have not been very popular among astronomers. Major reasons are probably the inherent observational difficulties and the comparatively low rates of discovery. In the past, with 4-m class telescopes, tens of hours of monitoring of several galaxies have indeed been necessary to detect a few distant novae [3].
VLT observations of NGC 1316 in the Fornax Cluster
NGC 1316 is a giant "dusty" galaxy (ESO Press Photo eso0024), located in the Fornax cluster seen in the southern constellation of that name ("The Oven"). This galaxy is of special interest in connection with current attempts to establish an accurate distance scale in the Universe.
In 1980 and 1981, NGC 1316 was the host of two supernovae of type Ia, a class of object that is widely used as a "cosmological standard candle" to determine the distance to very distant galaxies, cf. ESO Press Release eso9861. A precise measurement of the distance to NGC 1316 may therefore provide an independent calibration of the intrinsic brightness of these supernovae.
The new observations were performed during 8 nights distributed over the period from January 9 to 19, 2000. They were made in service mode at the 8.2-metre VLT/ANTU telescope with the FORS-1 multi-mode instrument, using a 2k x 2k CCD camera with 0.2 arcsec pixels and a field of 6.8 x 6.8 arcmin 2. The exposures lasted 20 min and were carried out with three optical filters (B, V and I).
The most distant Novae observed so far
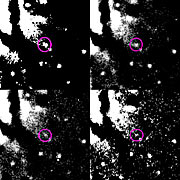
An analysis of the images that were obtained in blue light (B-filter) resulted in the detection of four novae. They were identified because of the typical change of brightness over the observation period, cf. eso0024b, eso0024c, as well as their measured colours.
Although the time-consuming reduction of the data and the subsequent astrophysical interpretation is still in progress, the astronomers are already now very satisfied with the outcome.
In particular, no less than four novae were detected in a single giant galaxy within only 11 days . This implies a rate of approximately 100 novae/year in NGC 1316, or about 3 times larger than the rate estimated for the Milky Way galaxy. This may (at least partly) be due to the fact that NGC 1316 is of a different type and contains more stars than our own galaxy.
The novae in NGC 1316 are quite faint, of about magnitude 24 and decreasing towards 25-26 during the period of observation. This corresponds to nearly 100 million times fainter than what can be seen with the naked eye. The corresponding distance to NGC 1316 is found to be about 70 million light-years .
Moreover, the discovery of four novae in one galaxy in the Fornax cluster was possible with only 3 hours of observing time per filter. This clearly shows that the new generation of 8-m class telescopes like the VLT, equipped with the new and large detectors, is able to greatly improve the efficiency of this type of astronomical investigations (by a factor of 10 or more), as compared to previous searches with 4-metre telescopes.
The road is now open for exhaustive searches for novae in remote galaxies, with all the resulting benefits, also for the accurate determination of the extragalactic distance scale.
Notes
[1] The group consists of Massimo Della Valle (Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Firenze, Italy), Roberto Gilmozzi and Rodolfo Viezzer (both ESO).
[2] A graphical illustration of the nova phenomenon can be found at this website.
[3] For example, in 1987, Canadian astronomers Christopher Pritchet and Sidney van den Bergh , in an heroic tour de force with the 4-metre Canada-France-Hawaii telescope, found 9 novae after 56 hours of monitoring of 3 giant elliptical galaxies in the Virgo cluster of galaxies.
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0024 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 17/00 |
| Name: | Fornax Cluster, NGC 1316 |
| Type: | Local Universe : Star : Type : Variable : Nova Local Universe : Galaxy : Type : Lenticular Local Universe : Galaxy : Type : Elliptical Local Universe : Galaxy : Size : Giant |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | FORS1 |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.