WFI Overview
The WFI is a joint project between the European Southern Observatory(ESO), the Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie (MPI-A) in Heidelberg (Germany) and the Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte (OAC) in Naples (Italy).
WFI in a Nutshell
| Field of view | 34'x33' |
| Pixel scale | 0.238 arcsec/pixel |
| Detector | 4x2 mosaic of 2kx4k CCDs |
| Filling factor | 95.9% |
| Read-out time | 27 seconds |
| Read-out noise | 4.5 e-/pixel |
| (Inverse) gain | 2.0 e-/ADU |
| Dynamical range | 16 bit |
| Full-well capacity | >200,000e- |
| Telescope aperture | 2.2 m |
| Telescope focus | Cassegrain (f/8) |
| Instrument F ratio | 5.9 |
| Wavelength range | Atmospheric cutoff to 1 micron |
| Intrinsic image quality | 0.4 arcsec |
| Geometrical distortions | <=0.08% |
| Slitless spectroscopy | 4.5 (5.7) nm resolution at 400-640 (650-850) nm |
| Raw data format | FITS (with extensions), 142 Mbyte/file |
The WFI chips and corresponding pixel values
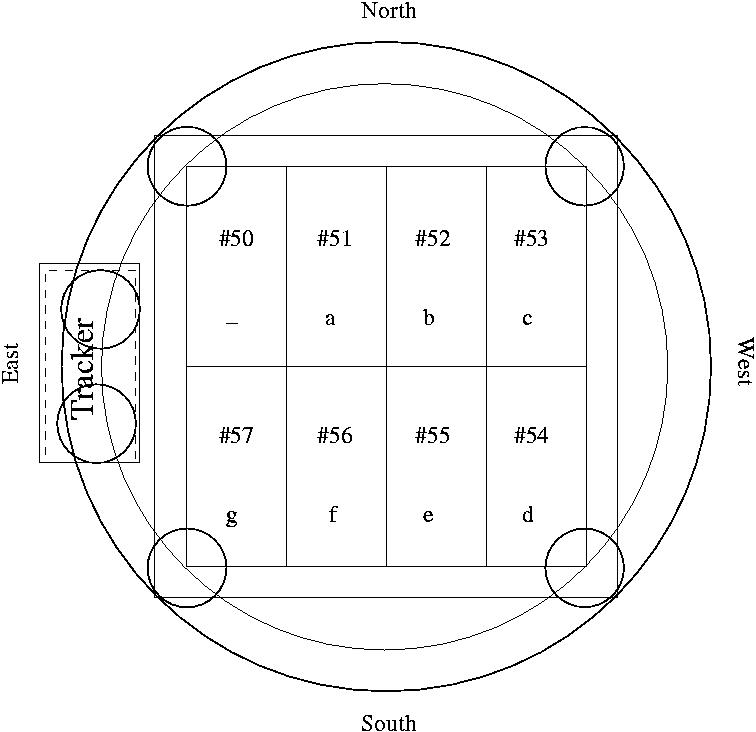
In the full field of view of the RTD, the southeasterm most light-sensitive pixels of each CCD fall on the following X/Y coordinates:
| CCD No. | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 2 | 4130 |
| 51 | 2149 | 4127 |
| 52 | 4293 | 4125 |
| 53 | 6437 | 4128 |
| 54 | 6437 | 3 |
| 55 | 4292 | 1 |
| 56 | 2149 | 1 |
| 57 | 5 | 6 |
The WFI gaps

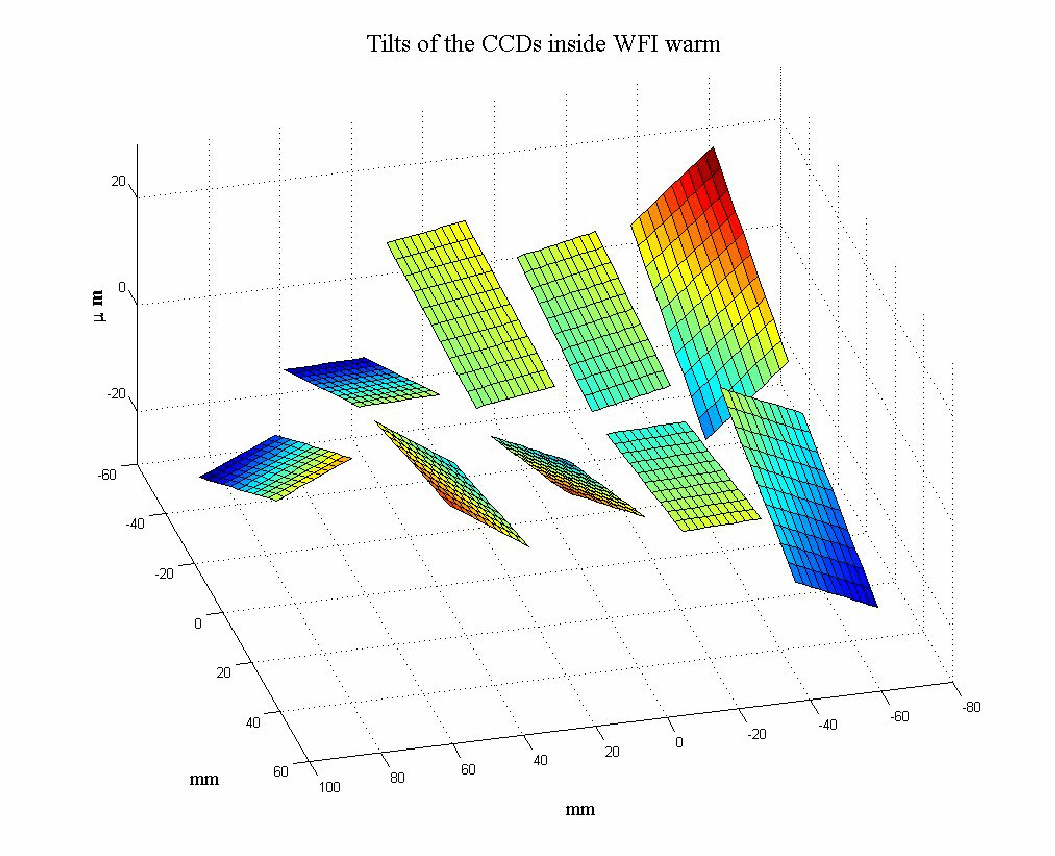
WFI Topography