Subsystem Simulator(supSimulator)¶
The Subsystem Simulator mimics the respond of a generic subsystem process. It is used to have an independent validation of the standard interface used between the System Supervisor and subsystems. The Subsystem Simulator is a dummy RAD based application which implements the standard state machine and the standard interface together with few specific features.
Note
From now on we will use the term Simulator to refer to the Subsystem Simulator.
The Simulator uses the OLDB to store run-time information. The Simulator publishes its own status following the requirements for interacting with the System Supervisor.
Command Line Arguments¶
Command line argument help is available under the option --help.
--server-id ARG| -i ARG(string)Server id. If not specified uses the one included in the configuration file.
--config ARG| -c ARG(string)Application configuration file.
--log-level ARG| -l ARG(enum) [default: ERROR]Log level to use. One of ERROR, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE.
--log-prop-file ARG| -l ARG(string)Log property file.
--req-endpoint ARG| -l ARG(string)Server MAL Req/Rep endpoint (zpb.rr://<ipaddr>:<port>/).
Environment Variables¶
$CFGPATHUsed to resolve configuration file paths.
Simulator State Machine¶
The Simulator uses a state machine described in a SCXML format that is
interpreted by the state machine engine provided by the rad application framework.
(SCXML specification).
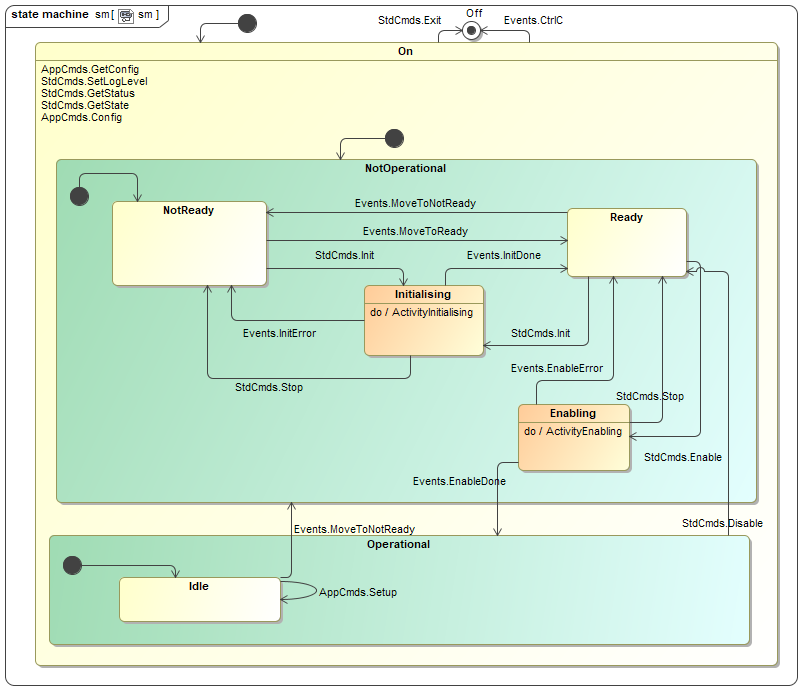
Simulator State Machine Diagram.¶
Off –> NotReady, event: Startup
The Simulator starts up and goes automatically to NotOperational/NotReady. Main server objects are instantiated including the basic application that uses the State Machine engine. The Simulator reads its own configuration and completes its initialisation.
NotReady –> Ready, event: Init
The Simulator moves from NotReady to Ready state by going through the Initialising transient state. During this transient state, the simulator will wait according to the configured delay time before to reply to the originator.
NotOperational/Ready –> Operational/Idle, event: Enable
The Simulator moves from NotOperational/Ready to Operational/Idle by going through the Enabling transient state. During this transient state, the simulator will wait according to the configured delay time before to reply to the originator.
Operational –> NotOperational/Ready, event: Disable
The Simulator is moved back to NotOperational/Ready substate.
NotOperational/Ready –> NotOperational/NotReady, event Reset
The Simulator is moved back to NotOperational/NotReady substate.
Configuration¶
SubSystem Simulator Configuration¶
The server configuration in version 4.0.0 has been ported to the CII config-ng library. Unlike yaml-cpp, this library allows to define type information for the configuration parameters. The Simulator includes a predefined set of configuration definitions. These files can be found in the subsim/server/resources/config directory.
You can find more information about CII config-ng in the following link. (Config-ng manual).
server::server_id
This is the id associated with the specific server. This id is used to associate all server configuration parameters as well as the prefix for the DB keys.
server::req_endpoint
This is the endpoint for CII MAL request/reply. The server will listen to incoming commands using this endpoint.
server::pub_endpoint
This is the endpoint for CII MAL pub/sub. The server will publish device topics using this endpoint.
server::db_timeout
This is the server timeout for connecting to the OLDB.
server::scxml
This is the state machine specification file used by the server.
server::req_timeout
General command timeout.
server::log_properties
Log4cplus property configuration file.
server::commands
This is the vector of commands active in the Simulator configuration. Only commands listed here will be managed by the Simulator.
Each command has its own set of configuration parameters
<command id>::reply_ok
This is a flag to indicate if command replies successfully or not. When it is true, the command replies ok otherwise it returns with an error.
<command id>::reply_delay
This is the delay in milliseconds to be used to reply to the originator.
<command id>::reply_ok_message
This is the message to be used when replying successfully.
<command id>::reply_error_msg
This is the message to be used when replying with an error.
<command id>::reply_error_code
This is a flag to enable/disable accessibility of a subsystem.
An example of a server configuration is provided below.
!cfg.include config/sup/subsim/server/definitions.yaml:
server: !cfg.type:SubSim
server_id : 'subsim1'
req_endpoint : "zpb.rr://127.0.0.1:15086/"
pub_endpoint : "zpb.ps://127.0.0.1:15046/"
db_timeout : 2000
log_properties : "config/utils/bat/log_properties.cfg"
scxml : "config/sup/subsim/server/sm.xml"
oldb_prefix : "ins1"
commands: [
{
name: 'Init',
reply_ok: true,
reply_delay: 3000,
reply_error_msg: "Init failed - subsystem could not initialize"
},
{
name: 'Enable',
reply_ok: true,
reply_delay: 3000,
reply_error_msg: "ERROR: Enable failed"
},
{
name: 'Disable',
reply_ok: true,
reply_delay: 3000,
reply_error_msg: "ERROR: Enable failed"
},
]
Simulator OLDB¶
The simulator stores the actual values of the server configuration parameters into the OLDB . This helps to verify whether the configuration has been loaded correctly. For details of the server configuration parameters, see :ref: sup_sim_config_ref_.
OLDB Key |
|---|
<server id>/cfg/db_timeout |
<server id>/cfg/dictionaries |
<server id>/cfg/req_timeout |
<server id>/cfg/mon_timeout |
<server id>/cfg/filename |
<server id>/cfg/pub_endpoint |
<server id>/cfg/req_endpoint |
<server id>/cfg/scxml |
<server id>/cfg/server_id |
<server id>/cfg/<command id>/reply_delay |
<server id>/cfg/<command id>/reply_error_msg |
<server id>/cfg/<command id>/reply_ok |
Commands¶
Error Handling¶
Simulator commands throw an exception (subsimif::ExceptionErr) in case of errors or timeouts from Simulator specific commands. For standard commands, the server throws a stdif::Exception. Client applications can catch the exceptions and obtain the error message associated with the function getDesc(). This error does not contain neither the history nor the error stack but it normally indicates precisely where the error occurred.
try {
auto reply = client->GetState();
} catch (const stdif::ExceptionErr& e) {
RAD_LOG_ERROR() << "Error reply " << e.getDesc() << ").";
}
Serialization¶
The Subsystem Simulator uses the CII MAL ZPB (ZeroMQ + Google Proto buffers) for serialising commands.
Note
Each command has two parts: a payload and its corresponding reply, see the details in the supif module. The normal replies are plain strings.
Sever Commands¶
The commands (events) currently supported by the Simulator are:
Command |
Parameters |
Interface |
|---|---|---|
Init |
“” |
stdif |
Enable |
“” |
stdif |
Disable |
“” |
stdif |
Reset |
“” |
stdif |
GetState |
“” |
stdif |
GetStatus |
“” |
stdif |
Exit |
“” |
stdif |
SetLogLevel |
“<ERROR|INFO|DEBUG|TRACE>” |
subsimif |
Setup |
“” |
subsimif |
Config |
“<config buffer>” |
subsimif |
GetConfig |
“” |
subsimif |
GetConfig Command¶
The GetConfig command returns the actual configuration used by the Simulator. This command is useful when starting the process with Nomad where configuration might be rendered.
Publishing¶
The Subsystem Simulator publishes as any other subsystem its state/substate. This is a requirement for enable visibility from the System Supervisor.
Parameter |
end point |
|---|---|
status |
<ps endpoint>/std/status |
Troubleshooting¶
Logging¶
The Subsystem Simulator implements logging levels according to the log4cplus package where the concept is:
ALL < TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL < OFF
The basic log levels supported by the Simulator for troubleshooting are listed in the table below.
Name |
Verbosity |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ERROR |
very low |
Provide logging only in case of errors. |
INFO |
low |
Provide information for the most important actions. |
DEBUG |
medium |
Provide additional information for the developer. |
TRACE |
very high |
Includes all the function tracing. |
C++ Simulator Client¶
The client application (supsimClient) is a simple utility allowing to send messages to the Simulator from
the command line. In this context we use the words messages and events as synonyms.
The supDummyClient uses two interface module (stdif and supsimif) to compose the payload of the messages. For
simplicity purposes, the associated interface for each command is hidden to the user.
The supsimClient sends the messages using CII MAL request/reply.
Note
This client uses the synchronous version of the stdif and supsimif interfaces.
$ supsimClient <serviceURI> <command> ["<parameters>"]
Where
<serviceURI> destination of the command (e.g. zpb.rr://127.0.0.1:12081)
<command> command to be sent to the server (e.g. Init)
<parameters> optional parameters of the command.
Examples¶
$ supsimClient zpb.rr://134.171.3.48:30519 Init
Note
The Config command is not supported by the C++ client.
Python Client Library¶
It is possible to communicate with the Subsystem Simulator through clients developed in
Python. The Simulator provides a library that simplifies the interaction with the System Supervisor (clib).
Users might want to interact directly with Supervisor ICD binding methods. This is, of course possible, but it is outside the scope of this library.
Note
The Supervisor python library uses the synchronous mal interface.
Error Handling¶
The clib reports as a RuntimeError exceptions that may be delivered by the Simulator.
Classes¶
The clib library provides one class that encapsulates the interface with the Supervisor.
This class is the SubsimCommands class.
SubsimCommands¶
The constructor of the SubsimCommands class support two parameters: uri and timeout. The timeout is optional and has a default of one minute, expressed in milliseconds.
The class handles two MAL client interfaces to deal with standard commands and Simulator specific commands. The correct interface will be selected according to the method used so this is hidden to the user.
Methods for Command Interface¶
Method |
parameters |
interface |
|---|---|---|
setup |
None |
subsimif |
config |
None |
subsimif |
get_config |
None |
subsimif |
state |
None |
stdif |
status |
None |
stdif |
init |
None |
stdif |
enable |
None |
stdif |
disable |
None |
stdif |
reset |
None |
stdif |
stop |
None |
stdif |
Additional Methods¶
The SubsimCommands class provides additional methods which uses the Config command to facilitate the update of the configuration at run-time.
Method |
parameters |
interface |
|---|---|---|
cfgreply |
<cmd>, <flag> |
subsimif |
cfgdelay |
<cmd>, <delay> |
subsimif |
cfgerrmsg |
<cmd>, <msg> |
subsimif |
Simulator CLI¶
The Simulator CLI (supsimcli) provides a experimental command shell with simple
commands aiming to simplify the interaction with the Simulator. The Simulator shell can be invoked issuing the
command supsimcli.
Command Line Parameters¶
The supsimcli offers few command line parameters. If no parameters are specified. The supsimcli shell commands are not necessary using the same names as the MAL interfaces with the purpose to shorten the commands names.
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
–uri |
if the URI is specified, the subsimcli will use it to connect to the server |
–name |
When using nomad, one could specify the name of the service instead of the URI |
–module |
Custom interface library |
–class_name |
Custom command class name |
–timeout |
Timeout for CII MAL requests in ms |
–log_level |
log level (ERROR, INFO, DEBUG) |
–help |
Show the usage message |
Warning
The supsimcli shell assumes NOMAD/CONSUL services are up and running. If this is not the case then only –uri parameter can be used.
Note
The supsimcli shell was created for the Simulator but since it uses the standard interface, it can be used for any server implementing this interface, although only for the standard events like init, enable, disable, etc.
supsimcli --uri zpb.rr://134.171.3.48:30269
supsimSh>?
Available command list:
- cfgdelay
- cfgreply
- cfgerrmsg
- disable
- enable
- help
- init
- reset
- setloglevel
- setup
- get_config
- state
- status
Command |
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|---|
disable |
sends the disable (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
enable |
sends the enable (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
help |
print the list of supported commands |
|
init |
sends the init (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
reset |
sends the reset (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
state |
sends the GetState (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
status |
sends the GetStatus (stdif) event to the connected server |
|
setup |
sends the setup (subsimif) event to the connected server |
|
get_config |
sends the GetConfig (subsimif) event to the connected server |
|
cfgreply |
<cmd>,<true|false> |
Configure reply flag for a given command. If flag is true, the command will return successfully otherwise with an error. |
cfgdelay |
<cmd>,<delay> |
Configure reply delay for a given command in milliseconds. |
cfgerrmsg |
<cmd>,<msg> |
Configure reply error message for a given command. The reply flag has to be false to take any effect. |
setlogloevel |
<INFO|DEBUG|TRACE> |
sends the SetLogLevel (stdif) event to the connected server |
ctrl-d |
Stop the shell |
Setting Configuration Parameters¶
Forcing Init command to finalize with an error:
supsimSh> cfgreply Init,false
reply> = OK
supsimSh>
Changing delay time for Init command:
supsimSh> cfgdelay Init,3000
reply> = OK
supsimSh>