The C++ Standard Library
R.Abuter
06/02/96
C++ Standard Library History
- Belongs to C++ Standard proposed by ANSI/ISO
- Standard currently circulating for comments and review
- Incorporates Standard Template Library
- A major addition on the C++, starting from ARM
- Part of the gcc 2.7 distributed with VLT Software
Why interesting?
- General purpose components
- Extensible framework
- Reliable and efficient
- Standard
- Orthogonal
Library components
- language support
- diagnostics
- general utilities
- strings
- locales
- containers
- iterartors
- algorithms
- numeric
- input/output
- standard C Library facility with static type safety
Strings
- Automatic memory management
- Automatic resize when needed
- Clear syntax and semantics
- Support for iterators
- Allows redefinition of operations
Normal c program to find a file on CCS
ccsCOMPL_STAT ccsFindFile (const char *fileName,
char *filePath,
vltINT8 *mode,
vltUINT32 *size,
vltINT8 *dirFlag)
{
char myFile[128];
struct stat stbuf;
char *pwd,*pchar;
char *intRoot,*vltRoot,*vltData;
/* Initialization */
strcpy(filePath,"");
*mode = 0; *size = 0; *dirFlag = 0;
if ( fileName == (char *) NULL ) return(FAILURE);
if ( filePath == (char *) NULL ) return(FAILURE);
/*
* Check if file exist in the current directory
*/
if ( (pchar = strpbrk(fileName,"/")) != (char *) NULL)
{
pchar ++ ; strcpy(myFile,pchar);
}
else
strcpy(myFile,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success; }
/*
* Check if file exist as current sub-directory
*/
if ((pwd = getenv("PWD"))!= (char *) NULL)
sprintf(myFile,"%s/",pwd);
else
strcpy(myFile,"./");
strcat(myFile,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success; }
/*
* Check if file exist as sub-directory of current module
*/
strcpy(myFile,"../");
strcat(myFile,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success ;}
/*
* Check if file exist in INTROOT or VLTROOT
*/
if (ccsGetInstallPath(&vltRoot,&intRoot,&vltData) != FAILURE)
{
if (intRoot != (char *) NULL)
{
sprintf(myFile,"%s/%s",intRoot,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success ;}
}
if (vltData != (char *) NULL)
{
sprintf(myFile,"%s/%s",vltData,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success ;}
}
if (vltRoot != (char *) NULL)
{
sprintf(myFile,"%s/%s",vltRoot,fileName);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success ;}
}
}
/*
* File does not exist
*/
return(FAILURE);
exit_success:
strcpy(filePath,myFile);
*mode = stbuf.st_mode;
*size = stbuf.st_size;
if ((stbuf.st_mode & S_IFDIR) == S_IFDIR ) *dirFlag = 1;
return(SUCCESS);
}
c++ using the standard library
#include <string>
#include <iostream.h>
main(int argc , char **argv)
{
struct stat stbuf;
string fileName=argv[1];
// Check if file exist in the current directory
string myFile = fileName.substr(fileName.rfind("/")+1);
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success; }
// Check if file exist as current sub-directory
string pwd = getenv("PWD");
if ( pwd.empty() ) pwd = ".";
myFile = pwd + "/" + fileName;
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success; }
// Check if file exist as sub-directory of current module
myFile = "../" + filename;
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success; }
//Check if file exist in INTROOT or VLTROOT
char *intRoot,*vltRoot,*vltData;
if (ccsGetInstallPath(&vltRoot,&intRoot,&vltData) != FAILURE)
{
string svltRoot=vltRoot,sintRoot=intRoot,svltData=vltData;
if ( !sintRoot.empty() )
myFile = sintRoot + fileName;
if ( !svltData.empty() )
myFile = svltData + fileName;
if ( !svltRoot.empty() )
myFile = svltRoot + filename;
if (stat(myFile,&stbuf) == 0) { goto exit_success ;}
}
}
// File does not exist
return(FAILURE);
exit_success:
string filePath = myFile;
*mode = stbuf.st_mode;
*size = stbuf.st_size;
if ((stbuf.st_mode & S_IFDIR) == S_IFDIR ) *dirFlag = 1;
return(SUCCESS);
}
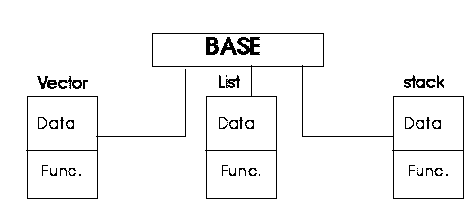
Containers Iterators and algorithms
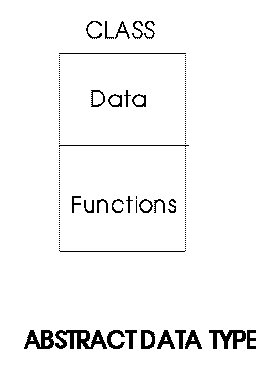
- Every application uses basic data structures like :
- Every application builds algorithms to access and manipulate those structures
- Every programmer reimplement code to do this
This library gives a general way to reuse code, define and manipulate these basic data structures
An OO Design Example
- Black-Box Algorithms
- Data access functions
- Sorting
- Searching
- Mutating
- Numerics
- Traverse backward/forward
- read/write/insert elements
STL approach
- Data structures=Containers
- Algorithms = Algorithms
- Access Functions = Iterators
An example :
Following a C++ program to sort a list of integers being readed from stdin :
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
// a and b point to integers. cmp returns -1 if a is less than b,
// 0 if they are equal, and 1 if a is greater than b.
inline int cmp (const void *a, const void *b)
{
int aa = *(int *)a;
int bb = *(int *)b;
return (aa < bb) ? -1 : (aa > bb) ? 1 : 0;
}
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
const int size = 1e5; // array of 100,000 integers
int array [size];
int n = 0;
// read an integer into the n+1 th element of array
while (cin >> array[n++]);
n--; // it got incremented once too many times
qsort (array, n, sizeof(int), cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << array[i] << "\n";
}
Simple version using containers iterators and algorithms:
#include <string.h> #include <algo.h> #include <vector.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream.h> main () { vector<int> v; // create an empty vector of integers int input; while (cin >> input) // while not end of filev.push_back (input); // append to vector sort(v.begin(), v.end()); int n = v.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << v[i] << "\n"; }
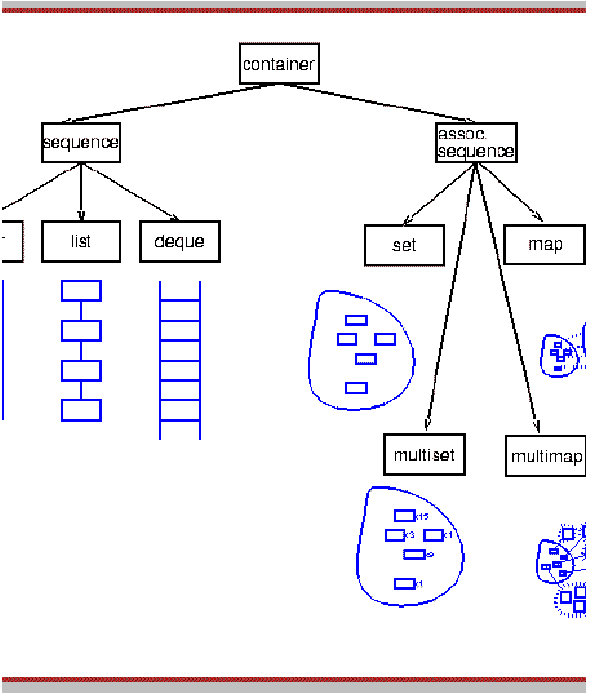
Containers attributes
- Contain other objects
- Do not depend on the object they contain
- Templated
- Provided by the library
- More can be coherently added
Iterators
- Common way for algorithms to access containers
- Pointer generalization
- Interface independent of type of container
- Traverse and read/write a container
- Every template function working with iterators work as well with pointers
Iterator types
1.-Input Iterator
2.-Output Iterators
3.-Forward Iterators
4.- Bidirectional Iterators
5.-Random Access Iterators
Algorithms
- Operate on containers
- Do not take containers as arguments
- Use iterators as arguments
- Template C++ functions
Some special STL components
Function Objects
- User defined functions
- To be used by algorithms
- Are implemented in classes with the () operator
- Context can be maintained in the class
Examples
Vectors :
#define _POSIX_SOURCE 1
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream.h>
#include <string>
#include <vector.h>
#include <algo.h>
struct stdCOMMAND {
string name;
string help;
int number;
void Output() const
{ cout << number << " - " << name << ": " << help << endl ; }
};
typedef vector<stdCOMMAND> stdCMD_VECTOR;
void ReadCommands(stdCMD_VECTOR& cmds)
{
stdCOMMAND cmd1;
// This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++
char tmpChar[256];
cout << "Enter command's definitions (--- to finish)\n";
while (true)
{
cout << "Name: ";
// This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++
// Should be correct just: cin >> cmd1.name;
cin >> tmpChar; cmd1.name = tmpChar;
if ( cmd1.name == string("---") )
break;
cout << "Help: ";
cin >> tmpChar; cmd1.help = tmpChar;
cout << "Num.: ";
cin >> cmd1.number;
cout << "Given command was: ";
cmd1.Output();
// Put cmd1 in the vector, using its name as key
cmds.push_back(cmd1);
}
}
void OutputCommands(stdCMD_VECTOR& cmds)
{
// -------------------------------------------------
// Use an iterator to print the whole dictionary
cout << "Current commands are:\n\n";
for (stdCMD_VECTOR::iterator i = cmds.begin();
i != cmds.end(); ++i)
{
//
(*i).Output();
}
cout << "\n\n";
}
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Following is a function object type,
// defines how to compare commands (for sorting/searching)
struct commandCompare {
bool operator()(const stdCOMMAND& a, const stdCOMMAND& b) {
return a.name < b.name; // based on names only
}
};
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Declares a comparison function object
commandCompare cmdComp;
int main(int, char *)
{
stdCMD_VECTOR cmds;
// -------------------------------------------------
// Fill the dictionary (vector)
ReadCommands(cmds);
// -------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the vector
sort(cmds.begin(), cmds.end(), cmdComp);
// -------------------------------------------------
// Print the dictionary (map)
OutputCommands(cmds);
// -------------------------------------------------
// Search in the dictionary for a given command
char tmpChar[256];
string key("");
cout << "Enter command's name for search (--- to finish)\n";
while (true)
{
cout << "Name: ";
// This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++
// Should be correct just: cin >> cmd1.name;
cin >> tmpChar; key = tmpChar;
if ( key == string("---") )
break;
// The correct way to check for existence
// of an entry
stdCMD_VECTOR::const_iterator i;
for ( i = cmds.begin();i != cmds.end(); ++i)
{
if ((*i).name == key )
{
cout << "Found: ";
(*i).Output();
break;
}
}
if(i == cmds.end())
cout << "Key: " << key << " not found!" << endl ;
}
return 0;
}
MAPS:
#define _POSIX_SOURCE 1 #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <iostream.h> #include <string> #include <map.h> #include <algo.h> struct stdCOMMAND { string name; string help; int number; void Output() const { cout << number << " - " << name << ": " << help << endl ; } };typedef map<string, stdCOMMAND, less<string> > stdCMD_MAP; void ReadCommands(stdCMD_MAP& cmds) { stdCOMMAND cmd1; // This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++ char tmpChar[256]; cout << "Enter command's definitions (--- to finish)\n"; while (true) { cout << "Name: "; // This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++ // Should be correct just: cin >> cmd1.name; cin >> tmpChar; cmd1.name = tmpChar; if ( cmd1.name == string("---")) break; cout << "Help: "; cin >> tmpChar; cmd1.help = tmpChar; cout << "Num.: "; cin >> cmd1.number; cout << "Given command was: "; cmd1.Output(); // Put cmd1 in the map, using its name as key cmds[cmd1.name] = cmd1; } } void OutputCommands(stdCMD_MAP& cmds) { // ------------------------------------------------- // Use an iterator to print the whole dictionary cout << "Current commands are:\n\n"; for (stdCMD_MAP::iterator i = cmds.begin(); i != cmds.end(); ++i) { // (*i) get the pair (key,value), so (*i).second extracts the value (*i).second.Output(); } cout << "\n\n"; } int main(int, char *) { stdCMD_MAP cmds; // ------------------------------------------------- // Fill the dictionary (map) ReadCommands(cmds); // ------------------------------------------------- // Print the dictionary (map) OutputCommands(cmds); // ------------------------------------------------- // Search in the dictionary for a given command char tmpChar[256]; string key; cout << "Enter command's name for search (--- to finish)\n"; while (true) { cout << "Name: "; // This is necessary because of a problem in libstdc++ // Should be correct just: cin >> cmd1.name; cin >> tmpChar; key = tmpChar; if ( key == string("---")) break; // The correct way to check for existence // of an entry stdCMD_MAP::const_iterator i = cmds.find(key); if(i == cmds.end()) cout << "Key not found!\n"; else { cout << "Key is: "; (*i).second.Output(); } } return 0; }
Conclusions
GOOD POINTS
- Generalize, clarify many concepts in use
- Orthogonal and complete without being too big
- Not binded to a single company
- Allow fast prototyping
BAD POINTS
- Poor documentation
- Standard not approved yet
- Compilers not fully supporting it yet
- Requires some knowlegde of C++
Library components
Language support
- Types
- Implementation properties ( limits )
- Start and Termination
- Dynamic memory management
- Type identification
- exception handling
- Other runtime support
Diagnostics
- Exception classes
- Assertions
- Error numbers
General Utilities
- Allocators ( encapsulate memory models )
- Utility components
- Function Objects ( via class with operator () )
- Dynamic Memory Management
- Date and time
Strings
- String classes
- Null-terminated sequence utilities
Localization
- Locales
- Standard locale Categories
- C library locales
Containers
- Sequence
- Associattive containers
Iterators
- Predefined iterators
- Stream Iterators
Algorithms
- Non-modifying sequence operations
- Mutating sequence operations
- Sorting and related operations
- C library algorithms
Numerics
- Complex numbers
- Numeric arrays
- Generalized numeric operations
- C library
- Forward declarations
- Standard iostream
- Stream buffers
- Formatting and manipulators
- String streams
- File streams