



Next: Cylindrical enclosure (VLT)
Up: Wind loading on
Previous: Results
The ESO NTT has been the first telescope whose enclosure is designed
to allow wind through-flow in the telescope volume (cf. section
 above). It has also become a kind of a standard
reference for advanced telescopes in the 4-m class.
The same design of telescope and enclosure
with minor modifications has
been adopted for the 3.5-m GALILEO telescope presently in
construction for installation at the observatory of La Palma
(Canary Islands) and is considered
also for a future South-African telescope.
above). It has also become a kind of a standard
reference for advanced telescopes in the 4-m class.
The same design of telescope and enclosure
with minor modifications has
been adopted for the 3.5-m GALILEO telescope presently in
construction for installation at the observatory of La Palma
(Canary Islands) and is considered
also for a future South-African telescope.
This enclosure is actually a real building, with several volumes and
rooms for telescope, instruments and auxiliary equipment which
rotates about the azimuth axis accompanying the telescope.
The telescope is housed in a kind of
corridor between two walls which separate the closed rooms for the
Nasmyth instruments which are air conditioned separately.
This corridor is closed on the front and upper sides
by 2 large upside-down-L shaped sliding doors while the back a wall includes
several louvers allowing through ventilation.
A semi-permeable windscreen can be raised across the
front side of the slit (fig.  ).
).
The tests were performed in the turbulent wind tunnel of the
Technical University of Aachen with a 1:50 model of the NTT
rotating building. The velocity measurements were taken at three
locations, indicated in fig. 4.8.
The tests were run with several venting configurations of the
enclosure

The measurements covered the range of azimuth angles from 0 to
60 with the wind direction.
Figs. 4.9 and 4.10 show the main results for
point TR45:
with the wind direction.
Figs. 4.9 and 4.10 show the main results for
point TR45:
- Mean speed
- Absolute turbulence intensity, evaluated with respect to
the free flow speed I

- Turbulence length scale, evaluated by approximating a Von Karman
spectrum (
 ) to the measured spectrum in the
inertial range. In this way the derived value of length scale will
best represent in parametric studies using the Von Karman expression
the actual energy density in the high frequency range most critical
for the telescope tracking performance.
) to the measured spectrum in the
inertial range. In this way the derived value of length scale will
best represent in parametric studies using the Von Karman expression
the actual energy density in the high frequency range most critical
for the telescope tracking performance.
- Fluctuation
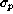 of the dynamic pressure term
of the dynamic pressure term
 .
.
The data show a sharp decrease of mean speed for azimuth angles
greater than 20 . Without windscreen (configurations O-O-O and
O-O-C), this is associated with a
large increase of turbulence, particularly for azimuth angles between
20 and 40
. Without windscreen (configurations O-O-O and
O-O-C), this is associated with a
large increase of turbulence, particularly for azimuth angles between
20 and 40 where the turbulent fluctuations of
the dynamic pressure created by the slit
are quite larger than in the free wind flow.
The turbulence length scale is respectively 0.8 and 1.4 of the
slit width at zero azimuth, which signifies the generation of high
frequency turbulence by the slit
edges even the telescope faces the wind directly.
Fig. 4.11 shows the result of a
computation of the pressure spectral density at 6 Hz for a free
flow mean speed of 18 m/s, a good indicator of
influence on the tracking performance as telescopes have generally
their first eigenfrequency between 5 and 8 Hz:
the amplification with respect to the free flow
conditions reaches one order of magnitude.
where the turbulent fluctuations of
the dynamic pressure created by the slit
are quite larger than in the free wind flow.
The turbulence length scale is respectively 0.8 and 1.4 of the
slit width at zero azimuth, which signifies the generation of high
frequency turbulence by the slit
edges even the telescope faces the wind directly.
Fig. 4.11 shows the result of a
computation of the pressure spectral density at 6 Hz for a free
flow mean speed of 18 m/s, a good indicator of
influence on the tracking performance as telescopes have generally
their first eigenfrequency between 5 and 8 Hz:
the amplification with respect to the free flow
conditions reaches one order of magnitude.
This effect is only corrected when the windscreen is raised to full
height across the front side of the slit, such that the mean flow
velocity, hence the pressure fluctuations on the telescope
(cf. equation ( )) are sharply decreased.
On the basis of these
results a 20% permeability windscreen was integrated in
the final design of enclosure. Observation records of the NTT at La
Silla show that in most cases the operator is obliged to raise it when
the wind when the wind exceeds about 6 m/s, that is almost half of the
time of observation.
)) are sharply decreased.
On the basis of these
results a 20% permeability windscreen was integrated in
the final design of enclosure. Observation records of the NTT at La
Silla show that in most cases the operator is obliged to raise it when
the wind when the wind exceeds about 6 m/s, that is almost half of the
time of observation.








Next: Cylindrical enclosure (VLT)
Up: Wind loading on
Previous: Results
Lorenzo Zago, zago@elgc.epfl.ch,
Sun Feb 26 22:57:31 GMT+0100 1995
 above). It has also become a kind of a standard
reference for advanced telescopes in the 4-m class.
The same design of telescope and enclosure
with minor modifications has
been adopted for the 3.5-m GALILEO telescope presently in
construction for installation at the observatory of La Palma
(Canary Islands) and is considered
also for a future South-African telescope.
above). It has also become a kind of a standard
reference for advanced telescopes in the 4-m class.
The same design of telescope and enclosure
with minor modifications has
been adopted for the 3.5-m GALILEO telescope presently in
construction for installation at the observatory of La Palma
(Canary Islands) and is considered
also for a future South-African telescope.





 with the wind direction.
Figs.
with the wind direction.
Figs. 
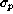 of the dynamic pressure term
of the dynamic pressure term
 .
.
 . Without windscreen (configurations O-O-O and
O-O-C), this is associated with a
large increase of turbulence, particularly for azimuth angles between
20 and 40
. Without windscreen (configurations O-O-O and
O-O-C), this is associated with a
large increase of turbulence, particularly for azimuth angles between
20 and 40 where the turbulent fluctuations of
the dynamic pressure created by the slit
are quite larger than in the free wind flow.
The turbulence length scale is respectively 0.8 and 1.4 of the
slit width at zero azimuth, which signifies the generation of high
frequency turbulence by the slit
edges even the telescope faces the wind directly.
Fig. 4.11 shows the result of a
computation of the pressure spectral density at 6 Hz for a free
flow mean speed of 18 m/s, a good indicator of
influence on the tracking performance as telescopes have generally
their first eigenfrequency between 5 and 8 Hz:
the amplification with respect to the free flow
conditions reaches one order of magnitude.
where the turbulent fluctuations of
the dynamic pressure created by the slit
are quite larger than in the free wind flow.
The turbulence length scale is respectively 0.8 and 1.4 of the
slit width at zero azimuth, which signifies the generation of high
frequency turbulence by the slit
edges even the telescope faces the wind directly.
Fig. 4.11 shows the result of a
computation of the pressure spectral density at 6 Hz for a free
flow mean speed of 18 m/s, a good indicator of
influence on the tracking performance as telescopes have generally
their first eigenfrequency between 5 and 8 Hz:
the amplification with respect to the free flow
conditions reaches one order of magnitude.



