EEV 44-82 -1-A57
CCD name : Caelum
Serial number :
9314-11-02
Type : Backside, Single layer AR Pixel size 15x15 µm
Number of photosensitive pixels 2048 x 4102 [HxV]
Number of
outputs : 2
Overall rating :
Test date : Tuesday January 9 2001
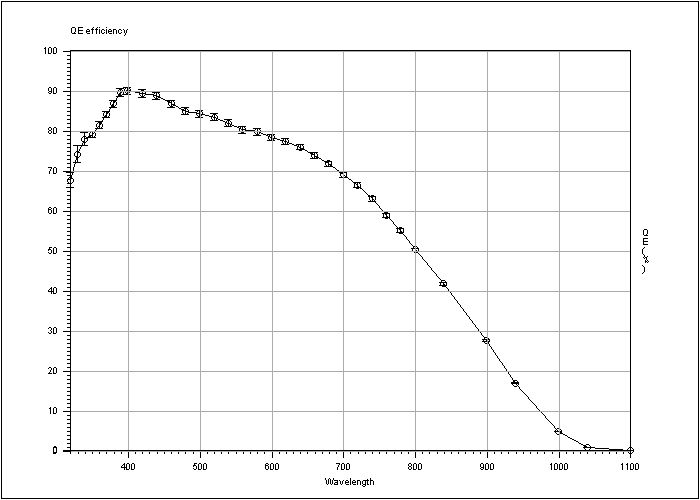
Clock mode: EEV 1p/225k/HG 512 Conversion Factor= 1.0239e-/ADU ±0.002837 for 24310.6ADU RMS noise = 6.8971e- ±0.05924 CCD temperature : -120.2Cº Window area is : X1= 67 X2= 2095 Y1= 3 Y2= 506 Bandwidth 5nm Wav. QE% PRNU rms% Phase= 320 67.6 ±1.9 3.1 6.990278 330 74.1 ±2.1 2.95 6.919618 340 77.9 ±1.5 2.88 6.883078 350 79 ±0.77 2.89 6.89571 360 81.3 ±0.8 2.92 6.914473 370 84 ±0.83 2.71 6.820794 380 86.7 ±0.86 2.27 6.592894 390 89.5 ±0.92 1.98 6.393495 400 89.9 ±0.91 1.8 6.24148 420 89.3 ±0.9 1.65 6.075473 440 88.6 ±0.89 1.6 6.016897 460 86.7 ±0.87 1.54 5.94352 480 84.8 ±0.85 1.49 5.899476 500 84.2 ±0.84 1.46 5.904783 520 83.3 ±0.84 1.41 5.880594 540 81.9 ±0.82 1.36 5.873096 560 80.2 ±0.8 1.32 5.9017 580 79.6 ±0.8 1.26 5.875542 600 78.3 ±0.78 1.21 5.876471 620 77.2 ±0.76 1.18 5.895203 640 75.9 ±0.74 1.16 5.932156 660 73.7 ±0.71 1.16 5.972717 680 71.7 ±0.68 1.18 6.04047 700 68.9 ±0.64 1.22 6.106016 720 66.3 ±0.61 1.34 6.232331 740 62.9 ±0.57 1.53 6.376133 760 58.7 ±0.53 1.53 6.385189 780 54.9 ±0.48 1.6 6.424183 800 50.2 ±0.43 1.69 6.501359 840 41.6 ±0.35 1.81 6.581016 900 27.5 ±0.22 2.22 6.798418 940 16.8 ±0.13 4.63 7.500237 1000 4.76 ±0.036 8.3 8.030088 1040 0.828 ±0.0062 8.41 8.05547 1100 0.108 ±0.0008 10.6 8.326909
Table 1: Measurement of the Quantum Efficiency.
Figure 1: Graphic representation of the QE.
Figure 2: Graphic representation of the PRNU.
In this section you can compare the QE we measured with the testbench and
QE Minimum specification
Typical QE
QE from Marconi
Figure 3: Comparison between the QE measured by ESO, the QE measured by Marconi,
ESO specification and minimum specification.
|
Comparison QE ESO / QE Marconi |
||||
|
Wavelength (nm) |
QE ESO (%) |
QE Marconi (%) |
Difference (Eso - Marc. %) |
Relative difference (Marconi as reference %) |
|
350 |
79 |
63.8 |
15.2 |
23.8 |
|
400 |
89.9 |
84 |
5.9 |
7 |
|
500 |
84.2 |
82 |
2.2 |
2.7 |
|
650 |
74.8 |
75.2 |
-0.4 |
-0.5 |
|
900 |
27.5 |
28 |
-0.5 |
-1.8 |
Table 2: Difference and relative difference between ESO measurement and Marconi.
Figure 4: Graphic representation of the difference and the relative difference.
For the flat field we use three wavelengths, 350nm, 600nm and 900nm. For each wavelength we make two images, high level (45000 ADU) and low level (1000 ADU).
350nm (UV), bandwidth 5nm |
600nm, bandwidth 5nm |
900nm, bandwidth 5nm |
|||
High level |
Low level |
High level |
Low level |
High level |
Low level |
Table 3: Flat field for three wavelengths.
The time exposure, for the long dark exposure, is 3600 seconds.
Table 4: Bias and dark.
Left readout port Conversion Factor= 0.56163e-/ADU ±0.001813 for 25474.7ADU RMS noise = 2.4803e- ±0.11 Right readout port Clock mode: 50kpx/4p/HG/512 Conversion Factor= 0.53092e-/ADU ±0.001675 for 26770.6ADU RMS noise = 2.6915e- ±0.1277 Right readout port Clock mode: EEV 1p/225k/HG 512 Conversion Factor= 0.51234e-/ADU ±0.001195 for 27664.7ADU RMS noise = 6.6897e- ±0.3355 Clock mode: 50kpx/4p/HG/512
RMS non linearity (%) = 0.193412 Peak to peak non linearity (%)= 0.601847
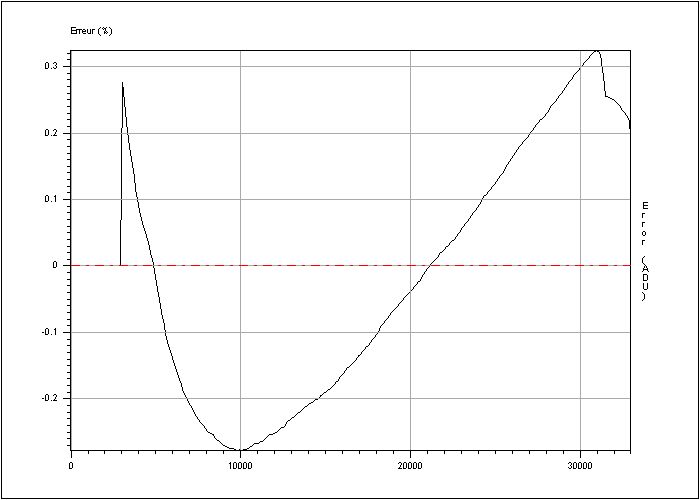
Figure 5: Error of linearity
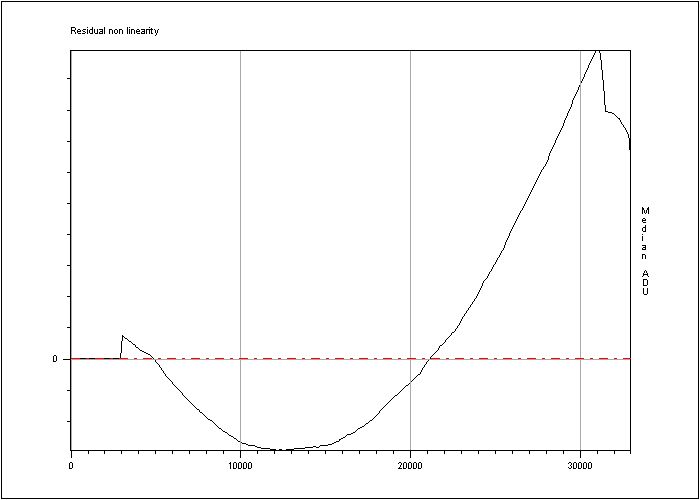
Figure 6: Residual non linearity.
Exposure time (s) = 3600 Dark current : 0.16 ± 0.01 e-/hour/pixel
Horizontal CTE = 0.999996 Vertical CTE = 0.9999994
In this section we expose the hot pixel, the dark pixel, the trap and the very large trap we found and how.
A hot pixel provides a signal of > 60 e- / pixel / hour.
Result: Eighteen hot points.
On our images these points are to the coordinates:
|
Position |
Image |
Histogram around the hot pixel |
X= 1418; Y= 0106 |
|
|
X= 1416; Y= 0174 |
|
|
X= 0570; Y= 0205 X= 0571; Y= 0205 X= 0572; Y= 0205 X= 0573; Y= 0205 X= 0574; Y= 0205 X= 0575; Y= 0205 X= 0576; Y= 0205 X= 0578; Y= 0205 X= 0579; Y= 0205 X= 0581; Y= 0205 X= 0580; Y= 0205 X= 0582; Y= 0205 X= 0584; Y= 0205 |
|
|
X= 0074; Y= 0370 |
|
|
X= 2040; Y= 0530 X= 2041; Y= 0530 |
|
|
Table 5: Position
and images of the hot pixels. The values in the table are in ADU and
the
conversion factor is 1.1 e-/ADU. All the point above 54 ADU
are hot points.
A dark pixel is one with 50% or less than the average output for uniform intensity light level, measured with a flat field level around 500 photo-electrons.
Result: Two dark pixels detected.
|
Position |
Image |
Histogram around the hot pixel |
|---|---|---|
X= 1945; Y= 2489 |
|
|
X= 0209; Y= 3167 |
|
|
Table 6: Position and images of the dark pixels. All the point under 747 ADU are dark points.
A trap is defined as a pixel that captures more than 10 electrons, measured with a flat field level around 500 photo-electrons.
Result: Not available
A very large trap is defined as a pixel that captures more than 10 000 electrons, measured with a flat field level around 90% of full well capability.
Result: See the section bad column. We have three very large trap.
A bad column is 10 or more contiguous hot or dark pixels in a single column or a very bright pixel or a very large trap.
Result: Three bad columns:
|
Position |
Image |
Histogram around the very large trap |
|---|---|---|
X= 1118; Y= 2678 |
|
|
X= 1091; Y= 3928 X= 1092; Y= 3927 |
|
|
Table7: Position and images of the bad column.
Here is a summary of cosmetic defects:
|
|
Hot pixel |
Dark pixel |
Trap |
Very large trap |
Bad column |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ESO |
18 |
2 |
/ |
3 |
3 |
|
Marconi |
58 |
5 |
1 |
3 |
|
Table 8: Summary of cosmetic defects.
Back to the overview page ESO Test Reports for the OmegaCAM CCDs